The Comprehensive Guide to Hydraulic Fitting Types
Our Blog
Comprehensive Guide
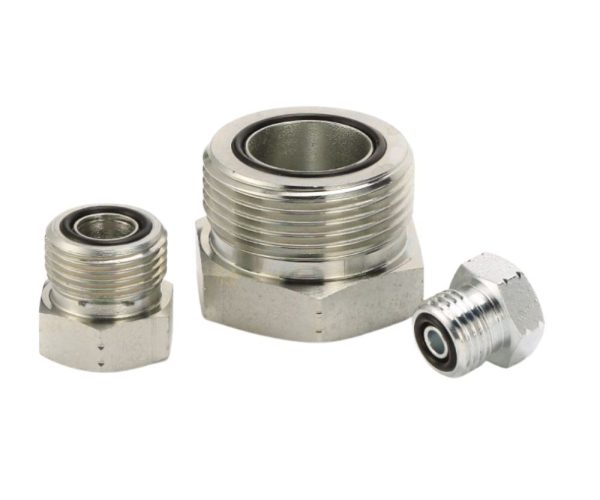
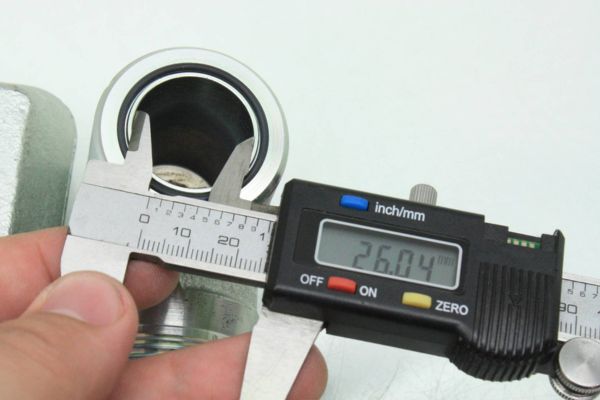
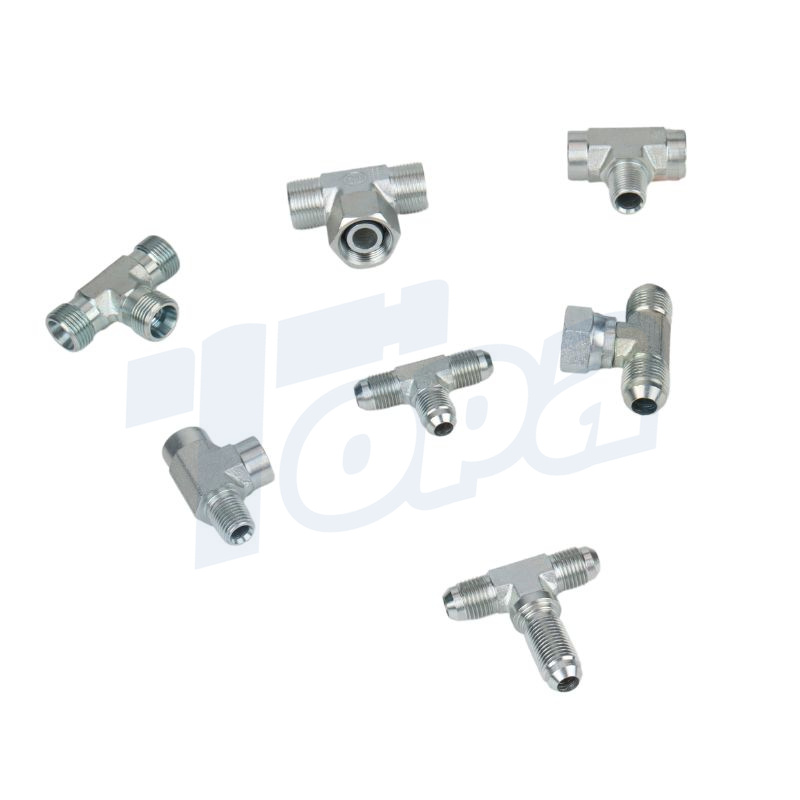
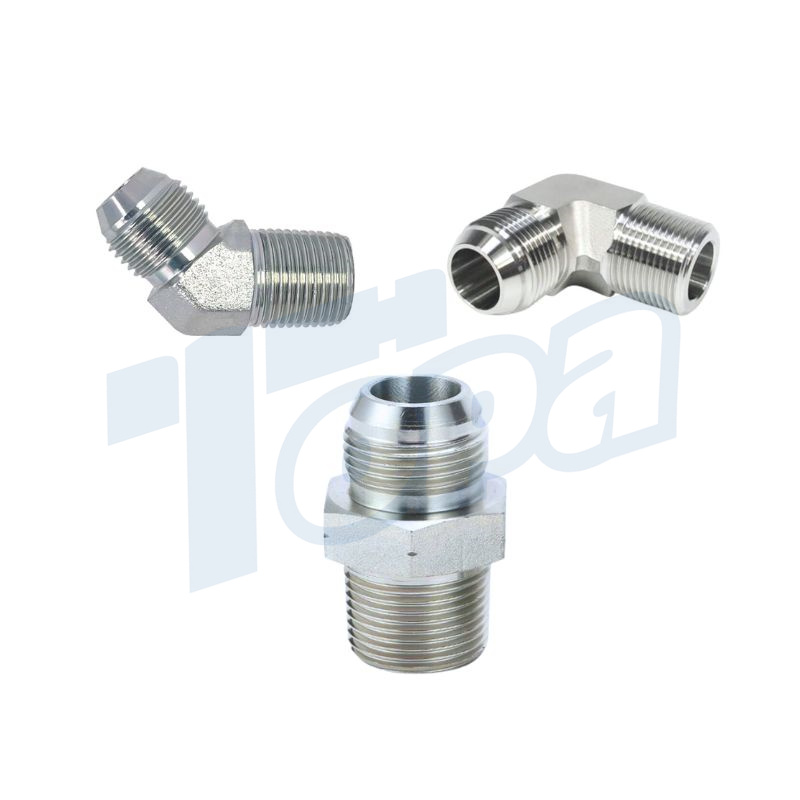
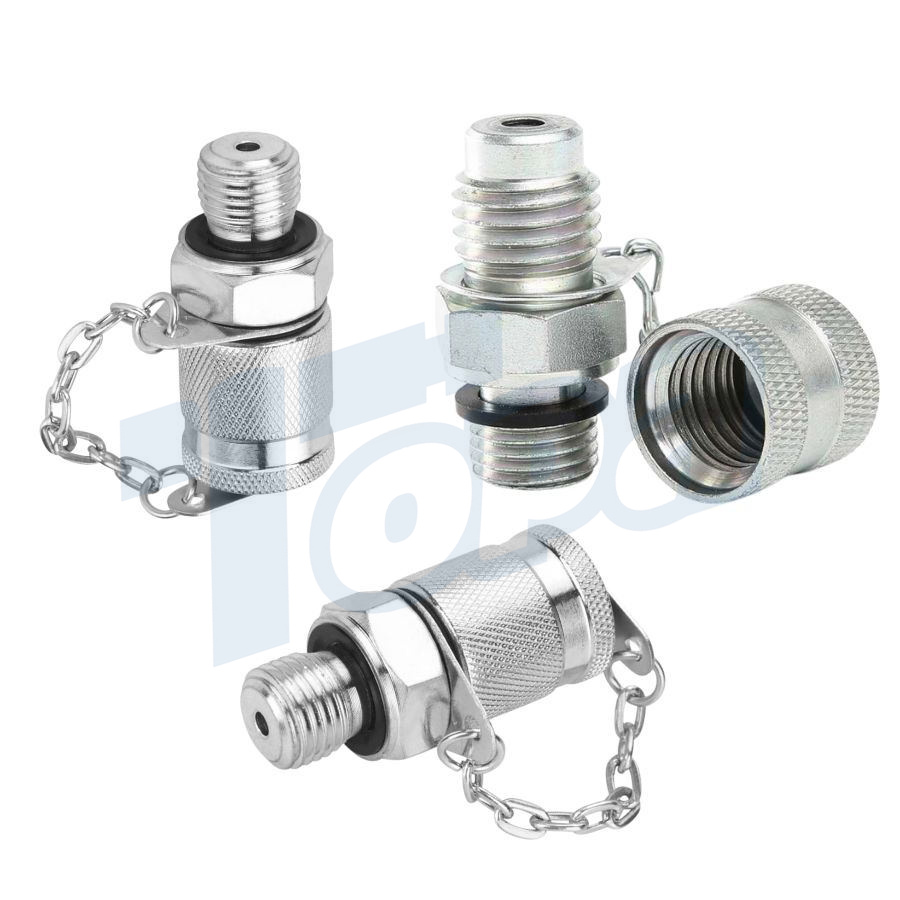
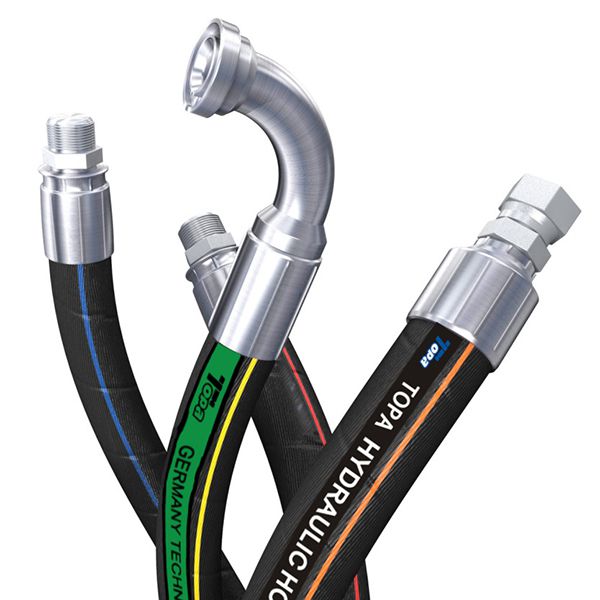
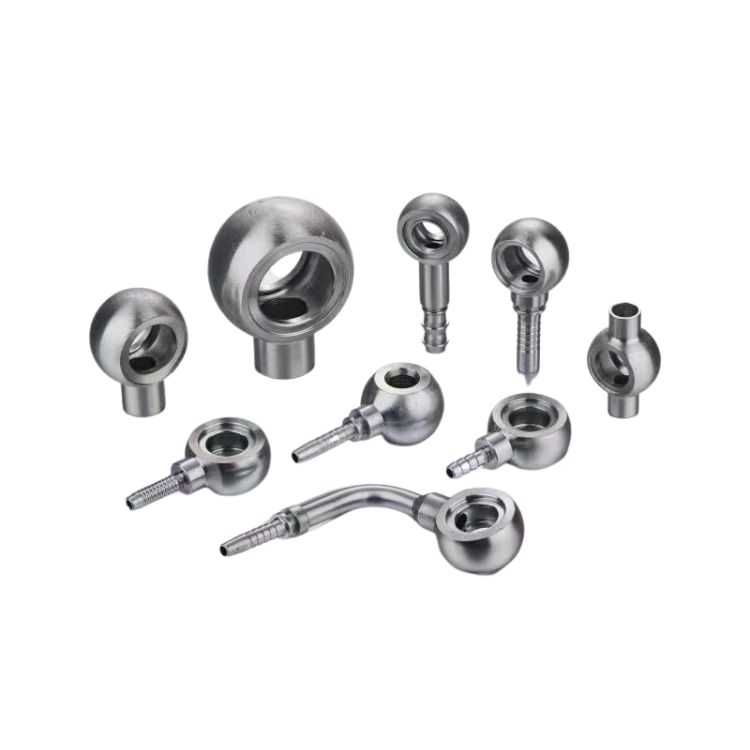
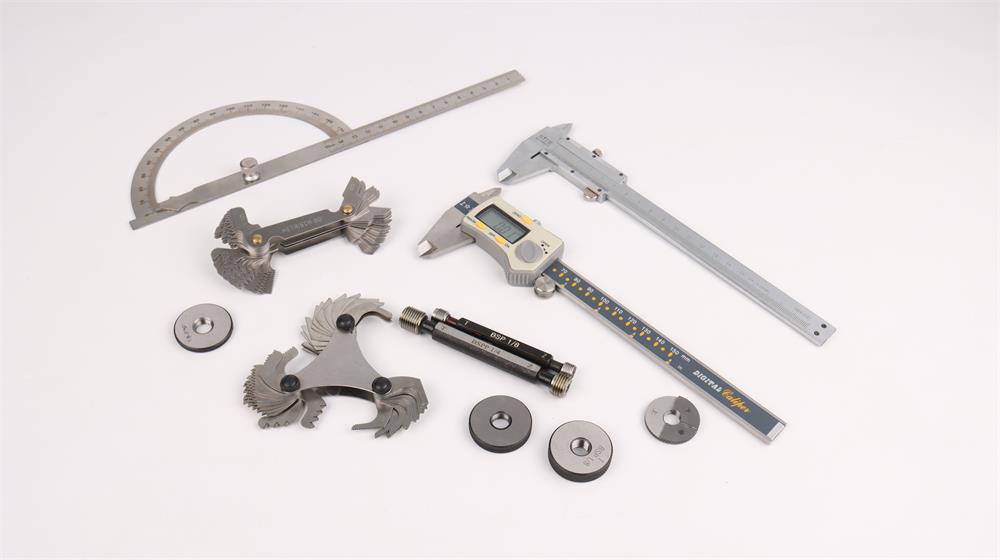
A comprehensive guide to hydraulic fitting types can help you learn more about threads such as JIC, BSP, SAE, JIS and NPT. This guide provides clear and practical advice to help you choose the right fitting for your hydraulic system. This guide all ensures that you have the knowledge you need to make informed decisions and maintain efficient, reliable operation.

Chapter 10
Pipe Thread vs Straight Thread Hydraulic Fittings

Chapter 11
JIC vs NPT Fittings: The Ultimate Guide
Chapter 12
SAE vs JIC Hydraulic Fitting: What's the Difference

Chapter 13
BSP VS NPT Threads:What are the Differences?

Chapter 14
UNC vs UNF Fittings: What is the Difference?
Your Questions?
Confused about the content of the article? Have any suggestions? Contact us and Topa will get back to you as soon as possible!