SAE vs JIC Hydraulic Fittings: What is the Difference?
In this guide, we’ll take an in-depth look at all aspects of JIC and SAE fittings, from their historical origins to their physical characteristics, performance specifications, and compatibility. Our goal is to equip you with the knowledge and insight you need to make an informed decision, ensuring you choose the right fitting for your specific hydraulic needs. So let’s begin this journey to better understand the intricacies of JIC and SAE hydraulic fittings.
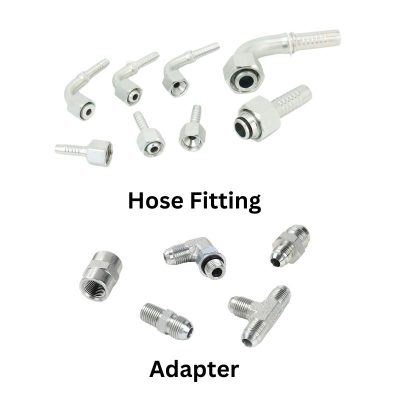
What is a Flare Fitting?
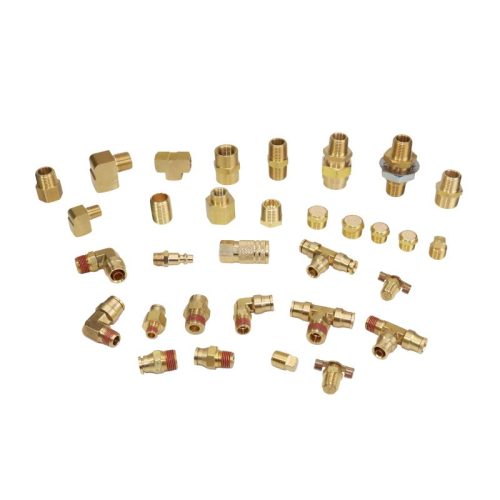
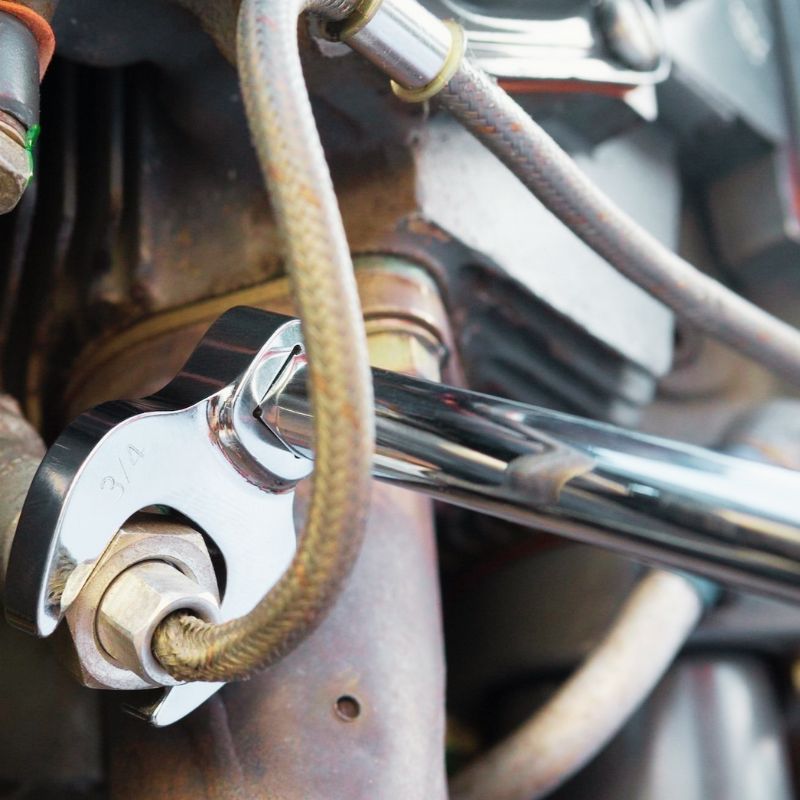
A flare fitting is more than just a simple connection in a hydraulic system, it is a critical component designed for high performance. These specialized fittings are used to connect tubing, hose or pipe to ensure a leak-proof seal that can withstand hydraulic conditions. The tip of the flare fitting has been engineered to include precise angles and dimensions to meet stringent industry standards. This not only ensures optimal performance of the fitting, but also provides long-term reliability, reducing the need for frequent maintenance or replacement.
Function of Flare Fittings
Flare fittings are essential in hydraulic systems for connecting various hydraulic components, from pumps and valves to actuators and cylinders. In this way, they allow hydraulic fluids to flow smoothly and efficiently throughout the system.
But flare fittings do more than just connect. These components are designed to maintain the overall efficiency and performance of the system. They do this by ensuring leak-proof seals, minimizing fluid loss and reducing the risk of contamination. It’s critical because even small leaks can lead to serious operational problems, including reduced system efficiency and increased maintenance costs.
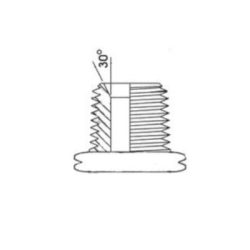
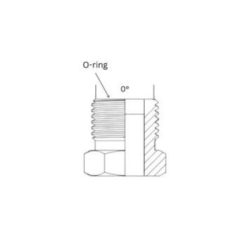
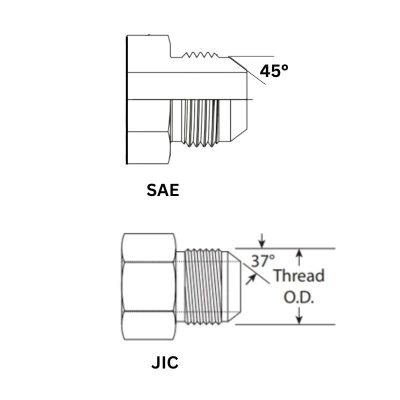
The most common hydraulic flare fittings are the JIC 37-degree tapered seat and SAE 45-degree flare fittings, both of which are described in more detail below.
Historical Background
Origins of the JIC Fitting
The Joint Industry Committee (JIC) fitting is a product of American ingenuity, originally developed to meet the stringent requirements of military applications. During World War II, the need for reliable, high-pressure fittings became critical. As a result, the JIC fitting was created and quickly adopted by the U.S. military for its durability and reliability under extreme conditions.
However, the JIC fitting’s use extends far beyond the battlefield. Over the years, JIC fittings have been used in a wide range of industrial applications. For example, they are commonly found in manufacturing environments, handling applications ranging from high-pressure fluid systems to pneumatic controls. The aerospace industry also relies heavily on JIC fittings for their ability to withstand high pressures and temperatures while maintaining a leak-tight seal.
Origins of SAE Flare Fittings
SAE flare fittings, on the other hand, were designed by the Society of Automotive Engineers, originally to meet the specific needs of the automotive industry. These fittings were designed to be versatile and cost-effective, making them ideal for automotive mass production. Their original applications included fuel lines, brake systems, and hydraulic clutches, among others.
However, the versatility of SAE flare fittings has led to their use in a variety of other areas as well. Today, they are commonly used in light industrial applications and heavy machinery. Their design allows for moderate pressure ratings, making them suitable for less demanding hydraulic systems. In addition, they can be used in refrigeration systems because they can handle a wide range of refrigerants.
Evolution of JIC and SAE Fittings
It’s important to note that both JIC and SAE fittings have come a long way over the years. Innovations in materials science have led to the development of more durable and corrosion-resistant fittings. This extends their service life and reduces the need for frequent replacement, resulting in long-term cost savings.
Physical Properties
Design
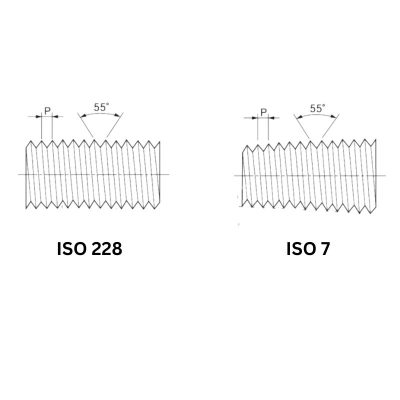
JIC: 37-Degree flare angle
JIC fittings have a 37-degree flare angle optimized for high-pressure applications. This specific angle makes for a stronger connection, reduces the risk of leakage, and ensures overall system reliability.
SAE: 45-degree flare angle
SAE fittings have a 45-degree flare angle. This design is better suited for medium-pressure conditions and is ideal for automotive and light industrial applications.
Thread size and pitch
JIC: JIC fittings typically have standardized thread sizes. This standardization ensures uniformity across applications and makes it easier for maintenance professionals to find alternatives. In addition, standardized threads help improve the fitting’s ability to form a secure, leak-tight connection, which is critical in high-pressure hydraulic systems.
SAE: SAE fittings use different methods, have uniform dimensional standards, and are available in a range of customizable thread sizes. This flexibility allows them to meet the specific needs of applications ranging from automotive to industrial environments.
Materials
JIC: JIC fittings contain stainless steel or brass materials. These materials offer excellent durability and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for long-term use in harsh environments. The choice of material usually depends on the application. Carbon steel fittings require different surface treatments for corrosion and acid resistance.
SAE: SAE fittings are typically made of carbon steel and offer a good balance of strength and cost-effectiveness. While carbon steel fittings are not as corrosion-resistant as stainless steel, they are often coated to increase durability and make them suitable for a variety of applications. However, SAE fittings are also available in other materials, depending largely on your needs.
Compatibility
Both JIC and SAE fittings are compatible with a variety of hydraulic systems. However, in some cases, a direct fit may not be feasible due to differences in design or thread size. In such cases, adapters with different threads can be used to bridge this gap and ensure a safe and reliable connection.
Pressure ratings
JIC: Known for their high pressure ratings, JIC fittings are the preferred choice for industrial, aerospace, and military applications. These industries often require hydraulic systems to operate under extreme conditions where even minor failures can have serious consequences. jic fittings are designed to meet these stringent requirements, providing a reliable, rugged solution.
SAE: In contrast, SAE fittings are designed for medium-pressure ratings. They are particularly well suited for automotive and light industrial applications, where hydraulic systems typically have lower pressure requirements. This makes SAE fittings a practical choice in these areas, balancing performance and cost.
Leak Resistance
JIC: One of the outstanding features of JIC fittings is their excellent leak resistance. These fittings are precision-engineered to minimize the risk of system failure due to leakage.
SAE: SAE fittings also offer good leakage resistance, but may require more frequent maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
Applications
JIC: JIC fittings are commonly used in a variety of industrial, aerospace, and military applications. Their high-pressure ratings and excellent leak-tightness make them ideal for these demanding applications.
SAE: SAE fittings are primarily used in automotive and light industrial applications. Their design and material selection make them suitable for these less demanding environments, balancing performance and cost.

Cost Effectiveness
JIC fittings have a high upfront cost but offer long-term value. Their durability and lower maintenance requirements mean they are actually more cost-effective over the entire life cycle of a hydraulic system. SAE fittings, on the other hand, are typically less expensive initially, but may need to be replaced more frequently, resulting in higher long-term costs.
Which is Better, JIC or SAE?
JIC fittings and SAE fittings are not superior or inferior, and much depends on the specific requirements of the hydraulic system. Both types of fittings have their advantages and limitations. The best choice depends on the specific needs of the hydraulic system, including factors such as pressure ratings, material compatibility, and long-term maintenance requirements. By understanding these nuances, you can make an informed decision that will improve the efficiency and reliability of your hydraulic system.
Can JIC and SAE be used interchangeably?
The short answer is no, it is not recommended to interchange JIC and SAE fittings. Although they may appear similar at first glance, these fittings have different design specifications and pressure ratings and are not intended to be used interchangeably.
How to Identify JIC and SAE Fittings?
Ensuring proper identification of JIC and SAE fittings is critical for optimal performance and safety of your hydraulic system. Below is a detailed step-by-step guide to help you accurately distinguish between the two types of fittings:
Tools Required
Protractor: These tools are essential for accurately measuring the flare angle of a fitting.
Thread Gauge: This tool helps you identify the thread size and pitch, another key feature that separates JIC and SAE fittings.
Step-by-step
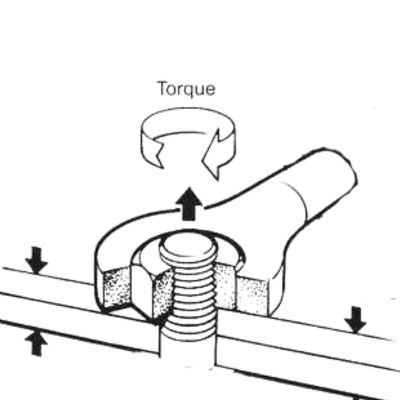
Visual Inspection
Begin with a careful visual inspection of the joint in question. Although JIC and SAE fittings appear similar at first glance, their flare angles are very different. In practice, however, it is difficult to tell the difference between a 37-degree and a 45-degree flare, and you will need to use the appropriate tool to measure them.
Measure Flare Angle
Use a protractor to measure the flare angle at the end of the fitting. This is a critical step because the flare angle is the most important feature that distinguishes these two types of fittings. There is also a special specialty angle gauge that allows for a direct comparison of JIC and SAE thread seating angles.
Check Thread Size and Pitch

Use a thread gauge to measure the thread size and pitch of the fitting. There are special fitting size tables as well as pitch tables, which you can compare to analyze once you have come up with the numbers with the help of a thread gauge.
Cross Reference
If you have access to any product documentation or specifications, verify the type of fitting against its measurements. Manufacturers often provide detailed information, including diagrams and specifications, to help you identify accurately.
Consult an Expert
When in doubt, it’s best to confirm with a hydraulic system expert or fitting manufacturer, who has the most detailed knowledge of hydraulic fittings. Incorrect identification can lead to system failure, increased maintenance costs, and even safety hazards.
How to buy JIC and SAE fittings?
Purchasing the right JIC or SAE fitting is a critical step in ensuring the optimal performance and safety of your hydraulic system. The following is a comprehensive guide to help you make an informed decision:
● Preliminary Steps
Determine your needs: Determine the specific requirements of your hydraulic system, such as pressure ratings, material compatibility, and type of application.
Review technical documentation: Review any technical specifications or system diagrams for the type and size of fittings required.
● Where to Buy
Authorized Distributors: Always buy from an authorized distributor or directly from the manufacturer to ensure that you are buying a quality product at the right price.
Web platforms: Ask for and buy hydraulic fittings from specialized hydraulic websites.
Trade shows and exhibitions: These events allow you to meet manufacturers and suppliers face-to-face, allowing you to evaluate products first-hand.
● Questions to ask the seller
Are these connectors certified to meet industry standards?
How long is the warranty?
Are volume discounts or trade accounts available?
What is the lead time?
Is after-sales support available?
● Final Steps
Place Order: After verifying all the details, place the order.
Quality Check: Upon receipt of the product, inspect the connector for any defects or discrepancies.
Installation: It is recommended that the connector be installed by a qualified technician to ensure proper installation.
Conclusion
For those who are still unsure about which accessories to choose, it is always a prudent step to consult with a hydraulic system specialist or manufacturer. At Topa, we aim to provide you with expert advice and high-quality solutions to meet your specific needs for hydraulic components.
Thank you for taking the time to read this guide. We hope it provides you with useful information to help you understand the complexities of JIC and SAE hydraulic fittings. Please feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need assistance.