How to Install and Tighten JIC Hydraulic Fittings
Introduction
JIC Hydraulic Fittings are an essential part of the hydraulic system and are the backbone of many operations in various industries. These fittings ensure the flow of hydraulic fluid, which is vital to the operation of a machine. This article is intended to guide readers through the meticulous process of properly installing and tightening JIC hydraulic fittings, an essential skill for maintaining the efficiency and safety of your hydraulic system.
Understanding JIC Hydraulic Fittings
The Basics of JIC Hydraulic Fittings
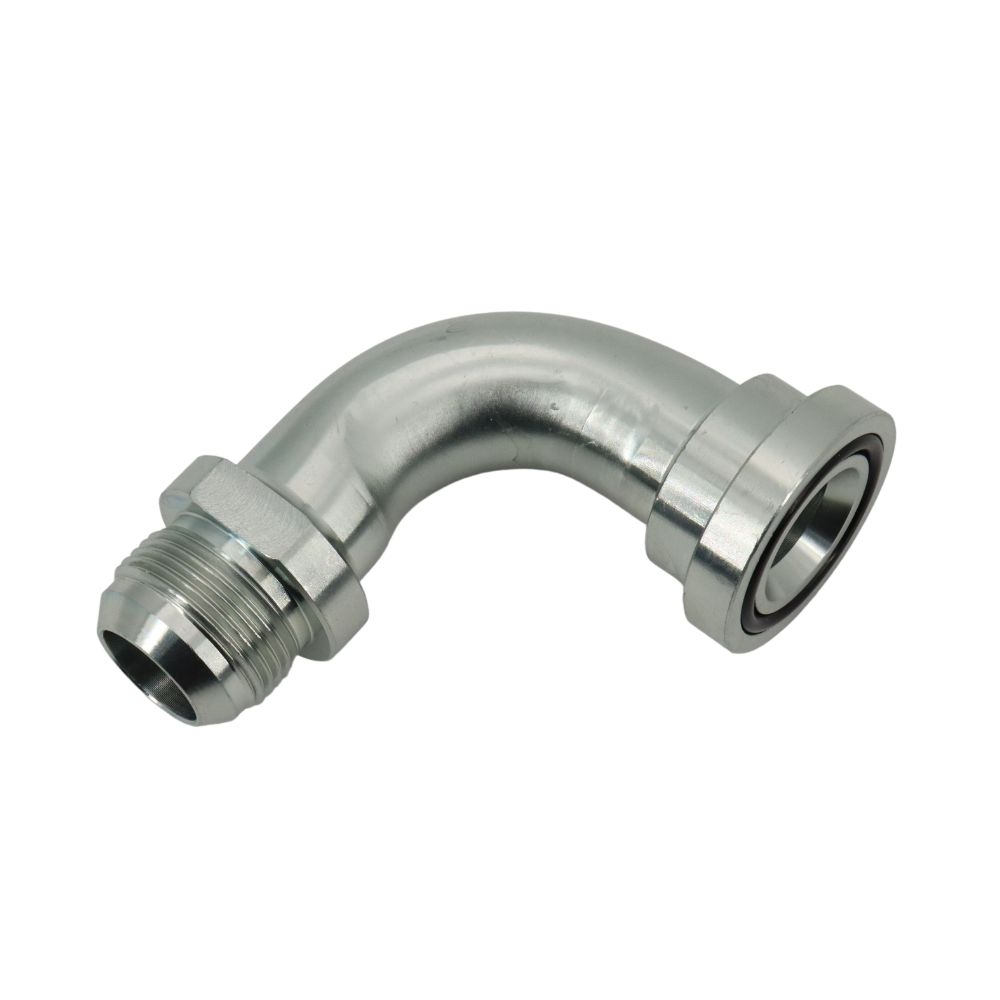
Hydraulic JIC fittings, standing for Joint Industry Council, are paramount in the hydraulic systems landscape, celebrated for their exceptional reliability and robustness. These fittings are engineered to endure high pressures and adverse conditions, a testament to their origins in the aerospace industry. The hallmark of JIC fittings is their 37-degree flare seating surface, a critical feature that facilitates the creation of secure, leak-proof connections.
Types of Hydraulic JIC Fittings
The diversity of JIC fittings serves as a cornerstone for their widespread application across various hydraulic systems, ensuring that there is a fitting type for virtually every possible scenario.
Straight Fittings
Straight JIC fittings are the most basic and commonly used type. They provide a direct connection between hydraulic hoses and components such as pumps, cylinders, and valves. They offer a straightforward solution for transferring fluid in a linear path without altering direction.
45-Degree Fittings
45-degree JIC fittings are designed to change the direction of the hydraulic line by 45 degrees. These fittings are invaluable in systems where space constraints prevent the use of straight lines or where a more gradual change in direction is beneficial to fluid dynamics. They help in minimizing the pressure drops and turbulence that can occur with sharper bends, ensuring a smoother flow of hydraulic fluid.
90-Degree Fittings
90-degree JIC fittings are essential for creating right-angle connections in hydraulic systems. They are particularly useful in tight spaces where bending a hose at a 90-degree angle would be impractical or could cause damage to the hose.
Bulkhead Fittings
Bulkhead JIC fittings are used to pass hydraulic lines safely and without leakage through bulkheads such as tanks or walls. They ensure system integrity while effectively separating components or parts of a hydraulic system.
Swivel Fittings
Swivel JIC fittings provide a pivoting connection point that can be rotated or moved without disassembling the fitting or twisting the hydraulic hose. These fittings reduce the risk of hose wear and leakage in applications where components need to move or rotate freely.
Tee and Cross Fittings
Tee and cross JIC fittings are used to branch hydraulic lines to distribute fluid from one source to multiple locations.
Applications of Hydraulic JIC Fittings
The utility of JIC fittings stretches across a broad spectrum of industries, marking them as indispensable components in fields as varied as agriculture, construction, and manufacturing. This widespread applicability is a testament to their versatility and the reliability they bring to hydraulic systems. Among the myriad advantages of JIC fittings are their ease of assembly and disassembly, which greatly simplifies maintenance and repair tasks. Additionally, their inherent resistance to vibration makes them an ideal choice for applications subject to constant movement or mechanical shock, ensuring that connections remain secure even in the most challenging conditions. The extensive range of sizes and configurations available further underscores the adaptability of JIC fittings, enabling their use in virtually any hydraulic system configuration one might encounter.
Pre-Installation Checklist
Before diving into the installation of hydraulic JIC fittings, it’s crucial to undertake thorough preparation. This preparation not only sets the stage for a smooth installation process but also ensures the safety and reliability of the hydraulic system. Let’s explore the essential steps, tools, and safety measures required to get started.
Tools Required
The installation of JIC fittings demands precision and the right set of tools. Each tool plays a significant role in ensuring that the fittings are installed correctly and securely. Here are some of the essential tools and their purposes:
Wrenches: Adjustable wrenches are indispensable for tightening and loosening fittings. Using two wrenches simultaneously — one to hold the fitting and the other to turn the nut — helps prevent the twisting of lines.
Tube Cutters: A clean, square cut on the hydraulic tube is vital for a leak-free connection. Tube cutters provide a precise cut, reducing the risk of leaks at the fitting interface.
Flaring Tools: For creating the 37-degree flare on tubing, a flaring tool is necessary. This flare matches the angled surface of the JIC fitting, ensuring a tight, leak-proof seal.
Deburring Tools: After cutting the tube, it’s essential to remove any sharp edges or burrs. Deburring tools ensure a smooth surface that won’t damage the sealing surface or O-ring.
Inspection Tools: Gauges and calipers are useful for verifying the dimensions of fittings and tubes, ensuring they meet the required specifications for a secure fit.
Safety Measures
Working with hydraulic systems requires a keen awareness of safety to prevent accidents and injuries. Here are some critical safety measures to observe:
Protective Gear: Always wear appropriate protective gear, including gloves, safety glasses, and steel-toed boots, to protect against hydraulic fluid spills and flying debris.
Depressurizing the System: Before starting any work, ensure the hydraulic system is fully depressurized. This step is crucial to prevent accidental discharge of hydraulic fluid under pressure.
Awareness of Surroundings: Be conscious of your environment, especially the potential for slipping on hydraulic fluids or tripping over equipment.
Fire Safety: Because hydraulic fluid is flammable, keep a fire extinguisher nearby and ensure the work area is well-ventilated to prevent the buildup of fumes.
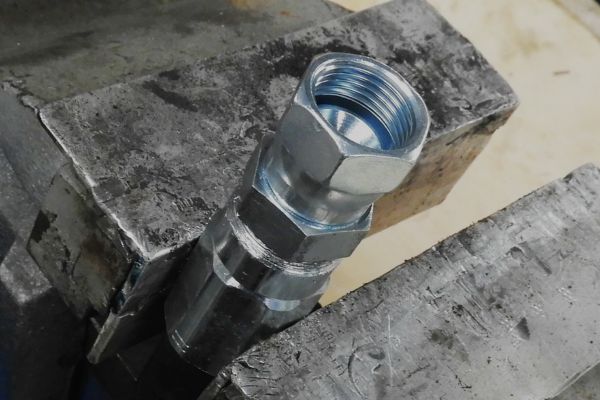

Preparing the Fittings and Hydraulic Lines
Proper preparation of the fittings and hydraulic lines is foundational to a successful installation. This process includes several key steps:
Inspection: Carefully inspect all fittings and hydraulic lines for any signs of damage, such as cracks, nicks, or corrosion. Damaged components should be replaced to avoid leaks or system failures.
Compatibility Check: Ensure that the fittings and hydraulic lines are compatible in size, material, and pressure rating. Mismatched components can lead to leaks or damage under pressure.
Cleaning: Remove any contaminants from the fittings and tubing. Cleanliness is critical to prevent dirt or debris from entering the system, which can cause wear or blockages.
Deburring: After cutting the tubing to the desired length, use a deburring tool to smooth the cut edge. This step is crucial to prevent damage to the sealing surfaces and ensure a leak-free connection.
Flaring: For tubing that requires flaring, use a flaring tool to create a 37-degree flare that matches the fitting. This precise angle is critical for a secure fit and leak-proof seal.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
Inspection
Objective: Ensure the compatibility and integrity of both hydraulic lines and fittings before installation.
Process: Carefully examine the hydraulic lines and fittings for any signs of damage, such as cracks, nicks, or any form of debris that might compromise the installation. Verify that the fittings match the hydraulic line in terms of size, type, and material.
Preparation
Objective: Prepare the hydraulic line for fitting installation.
Process: If necessary, use a tube cutter to cut the hydraulic line to the required length, ensuring a clean, square cut. After cutting, use a deburring tool to remove any sharp edges or burrs from the cut end of the line, creating a smooth surface for fitting installation.
Flaring (If Applicable)
Objective: Create a 37-degree flare on the hydraulic line to match the JIC fitting angle.
Process: Utilize a flaring tool to form a precise 37-degree flare at the end of the hydraulic line. This flare is essential for establishing a leak-proof seal with the JIC fitting.
Fitting Installation
Objective: Securely connect the fitting to the hydraulic line.
Process: Start by threading the fitting nut onto the hydraulic line, followed by threading the fitting itself. It’s important to hand-tighten the fitting initially to ensure proper engagement and alignment, avoiding cross-threading.
Tightening
Objective: Secure the fitting to the correct torque specification to ensure a leak-proof connection.
Process: Use two wrenches for this step — one to hold the fitting in place and the other to tighten the nut. This prevents the fitting from turning and potentially damaging the hydraulic line. Tighten the nut to the manufacturer’s recommended torque specification, being careful not to over-tighten, as this could strip the threads or damage the fitting and the line.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When installing JIC fittings, certain pitfalls can compromise the integrity and performance of the hydraulic system. Awareness and proactive measures can prevent these issues:
Cross-threading: This occurs when the fitting is not properly aligned with the thread of the port or hose. To avoid cross-threading, start threading by hand to ensure proper alignment. If resistance is felt, backtrack and realign rather than forcing the fitting.
Over-tightening: Excessive force can strip threads or deform the fitting and the sealing surface, leading to leaks or fitting failure. Adhering to the manufacturer’s torque specifications is crucial. Use a torque wrench whenever possible to apply the correct amount of torque.
Under-tightening: Insufficient torque can lead to leaks due to inadequate seal compression. Ensure that fittings are tightened to the recommended torque value, checking for leaks under pressure after installation.
Using Damaged Components: Inspecting all fittings and hydraulic lines for damage before installation is essential. Damaged threads, cracks, or deformities can prevent a proper seal, leading to leaks or system failure. Replace any damaged components before proceeding with the installation.
Troubleshooting Installation Issues
Leaks
Immediate Action: Verify that the fitting is tightened to the manufacturer’s recommended torque. Over- or under-tightening can lead to leaks.
Further Steps: If leaks persist after ensuring proper torque, disassemble the connection for a thorough inspection. Look for signs of damage to the threads, fitting, or tubing. Ensure no foreign material is present on the sealing surfaces. Re-install after ensuring all components are clean and undamaged.
Poor Fit
Verification: Double-check the compatibility of the fitting with the hydraulic line. This includes checking the size, type (male or female), thread pattern, and material. Incorrectly matched components can lead to poor fit and potential system failure.
Resolution: Replace any components that do not match exactly. Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for both the fittings and the hydraulic lines.
Pressure Drop
Investigation: A significant pressure drop post-installation could indicate several issues, such as under-tightening, which might not create a proper seal, or using an incorrect fitting type that does not match system requirements.
Diagnostic Steps: Check the entire system for any signs of leaks or improper fittings. Ensure all fittings are correctly tightened. If the issue persists, consult the system’s hydraulic schematic to verify that the correct type of fittings is used and that they are installed in the correct orientation.
Additional Troubleshooting Tips
Cross-Contamination: Ensure that different materials (e.g., stainless steel and carbon steel) are not used together in the same system to prevent galvanic corrosion.
Thread Damage: Inspect threads on both the fittings and the hydraulic lines for any signs of damage. Even minor thread damage can prevent a proper seal.
Use of Sealants: While JIC fittings are designed to seal without additional sealants, ensure no unauthorized sealants have been used, as they can cause issues with the hydraulic fluid and system performance.
Tightening Hydraulic JIC Fittings
Understanding the Tightening Process
The correct tightening of JIC hydraulic fittings is crucial to prevent leaks and ensure the longevity of both the fitting and the hydraulic system. Over-tightening can be as detrimental as under-tightening. The former can lead to deformation of the fitting, damage to the threads, or even cracking, while the latter may result in leaks or disconnection under pressure. Therefore, understanding and applying the correct torque is essential for a secure and reliable connection.
Tools for Tightening JIC Fittings
Torque wrenches are highly recommended for the tightening process as they allow for precise application of torque. These tools are critical in preventing over-tightening, ensuring that each fitting is tightened to the manufacturer’s specified torque value.
The Flats Method
The flats method is a commonly used technique for achieving the correct torque without a torque wrench, particularly in field conditions where precise tools may not be available. This method involves tightening the nut by a specific number of flat surfaces on the hex nut after finger-tightening. While useful, it’s less precise than using a torque wrench and can potentially lead to over-tightening if not done with care.
Final Inspection and Testing
After installation and tightening, conducting a thorough inspection and testing phase is critical. This includes checking for any signs of over-tightening such as thread damage, leaks, or any deformation of the fitting and tubing. Pressure testing the system can help verify that connections are secure and there are no leaks, ensuring everything is assembled correctly and functioning as intended.
Over-tightening JIC Hydraulic Fittings
Over-tightening JIC fittings can compromise the integrity of the hydraulic system. It can lead to damaged threads, compromised seal integrity, and even cracking of the fitting or flared end of the tubing. These issues can result in leaks and reduced system performance, and they may necessitate costly repairs or replacements. Therefore, it’s essential to follow the specified torque values and use the appropriate tools and techniques to avoid over-tightening.
Conclusion
The correct installation and tightening of JIC hydraulic fittings is vital to the efficiency of your hydraulic system. By following this guide, you can ensure that your systems are maintained to a high standard. If you still have any questions, feel free to contact Topa with your confusion!