BSP and JIC Hydraulic Fittings: A Comparative Analysis
In the complex landscape of hydraulic systems, choosing the right fittings is a decision that can significantly impact performance, reliability, and overall efficiency. With a myriad of options available, two types of fittings often stand out—JIC (Joint Industry Council) and BSP (British Standard Pipe). Both come with their unique features, advantages, and limitations. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the intricacies of JIC and BSP fittings, offering insights into their origins, features, applications, and how to identify and measure them.
JIC Fittings
Definition and Origin
The JIC (Joint Industry Committee) fitting is a hydraulic fitting that originated in the United States. Designed to meet standards set by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), it is commonly used in a variety of hydraulic applications.
Features
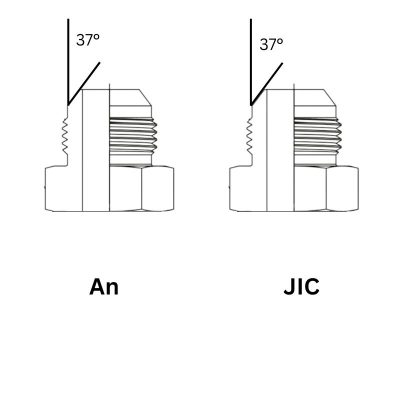
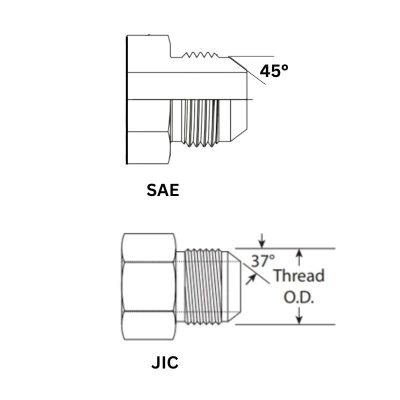
JIC fittings are known for their 37-degree flare seating surface, a key feature that distinguishes them from other types of hydraulic fittings. This design provides a strong metal-to-metal sealing surface. Also, JIC fittings have straight threads, and they are typically made of high-strength materials such as stainless steel, carbon steel, and brass, ensuring durability and reliability.
Typical Applications

JIC fittings are versatile and can be used in a variety of industries, including:
Construction machinery
Agricultural equipment
Automotive hydraulics
Industrial hydraulics
They are particularly useful in systems where high-pressure capabilities are required and leakage is a major concern.
Advantages
High-Pressure Handling: The 37-degree flare design allows JIC fittings to effectively handle high-pressure conditions.
Versatility: JIC fittings are compatible with a wide range of tubing and hose materials, making them highly versatile.
Easy to install: The design allows for quick and easy assembly and disassembly, saving time and labor costs.
Durability: JIC fittings are made of high-strength materials for durability, reducing the need for frequent replacement.
Disadvantages
Limited Material Options: Although durable, JIC fittings have limited material options compared to other fitting types.
Possibility of over-tightening: Metal-to-metal seals can sometimes be over-tightened, which can cause deformation and break the seal.
Dash | Thread | Threads Pre | Female Thread | Male Thread |
-2 | 5/16 | 24 | 6.7 | 7.9 |
-3 | 3/8 | 24 | 8.3 | 9.5 |
-4 | 7/16 | 20 | 9.9 | 11.1 |
-5 | 12 | 20 | 11.5 | 12.7 |
-6 | 9/16 | 18 | 12.7 | 14.3 |
8 | 3/4 | 16 | 17.5 | 19.1 |
-10 | 7/8 | 14 | 20.6 | 22.2 |
-12 | 1-1/16 | 12 | 24.6 | 27.0 |
-14 | 1-3/16 | 12 | 28.2 | 30.2 |
-16 | 1-5/16 | 12 | 31.4 | 33.3 |
-20 | 1-5/8 | 12 | 39.3 | 41.3 |
-24 | 1-7/8 | 12 | 45.6 | 47.6 |
-32 | 2-1/2 | 12 | 61.5 | 63.5 |
JIC hydraulic fittings size chart
BSP Fittings
Definition and Origin
BSP (British Standard Pipe) fittings are a globally recognized standard for connecting and sealing pipes and fittings. Originating from the United Kingdom, BSP threads have been adopted internationally and are based on ISO 228 and Whitworth standard threads. Developed in 1841, Whitworth threads were the world’s first screw thread standard, paving the way for BSP’s widespread adoption.
Features of BSP Fittings
BSP threads are rounded and have a 55-degree thread angle, which is different from the 60-degree angle found in NPT threads. BSP threads come in two styles—parallel (often referred to as “G” threads) and tapered (referred to as “R” threads). BSP fittings often use bonded ring seals or O-rings, providing a secure, leak-tight seal without the need for thread sealants.

Advantages
Global Acceptance: Due to their British origin and international standardization, BSP fittings are widely accepted and used globally.
Excellent Sealing Properties: BSP fittings offer superior leak-tight seals, especially when used with bonded rings or O-rings. This makes them highly efficient in high-pressure systems.
Ease of Installation: The design of BSP fittings allows for straightforward assembly and disassembly, saving time and reducing labor costs.
Material Versatility: BSP fittings are made from a variety of materials, including steel, stainless steel, brass, and even plastics, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
High-Pressure Ratings: BSP fittings are known for their ability to withstand high pressures, making them ideal for demanding hydraulic applications.
Disadvantages
Possibility of Leakage: While BSP fittings generally provide an excellent seal, metal-to-metal contact can sometimes lead to leakage if not installed properly.
Limited Availability in Some Areas: BSP fittings may not be readily available in areas where American standards are the norm.
Cost: High-quality BSP fittings made from premium materials can be more expensive than other types of fittings.
Thread | Threads | Pitch | Major diameter | |
Mm | Inch | |||
1/16 | 28 | 0.907 | 7.723 | 0.304 |
1/8 | 28 | 0.907 | 9.728 | 0.383 |
1/4 | 19 | 1.337 | 13.157 | 0.518 |
3/8 | 19 | 1.337 | 16.662 | 0.656 |
1/2 | 14 | 1.814 | 20.995 | 0.825 |
5/8 | 14 | 1.814 | 22.911 | 0.902 |
3/4 | 14 | 1.814 | 26.441 | 1.041 |
1 | 11 | 2.309 | 33.249 | 1.309 |
1 1/4 | 11 | 2.309 | 41.91 | 1.65 |
1 1/2 | 11 | 2.309 | 47.803 | 1.882 |
2 | 11 | 2.309 | 59.614 | 2.347 |
2 1/2 | 11 | 2.309 | 75.184 | 2.96 |
3 | 11 | 2.309 | 87.884 | 3.46 |
4 | 11 | 2.309 | 113.03 | 4.45 |
5 | 11 | 2.309 | 138.43 | 5.45 |
6 | 11 | 2.309 | 163.83 | 6.45 |
BSP hydraulic fittings size chart
Key Differences Between JIC and BSP Fittings
Design and Construction
JIC (Joint Industry Council) Fittings: Originating in the United States, JIC fittings are known for their 37-degree flare seating surface. They are commonly used in high-pressure hydraulic systems.
BSP (British Standard Pipe) Fittings: Originating in the United Kingdom, BSP fittings come in two main types: parallel (BSPP) and tapered (BSPT). They are known for their rounded threads and are widely used in fluid and gas applications.
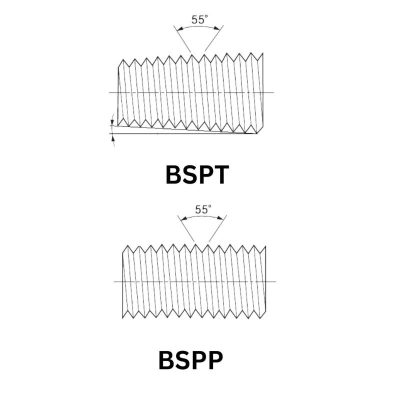
Comparison of the Design Features
JIC: The 37-degree flare seating surface ensures a metal-to-metal seal, which is highly effective in high-pressure systems.
BSP: The 30-degree cone seat, rounded threads, and the option for tapered threads provide a secure, leak-tight seal, especially when using bonded seals or O-rings.
Performance
JIC: Known for their high-pressure handling capabilities, making them ideal for hydraulic systems.
BSP: Known for their reliable sealing mechanisms, making them suitable for both high and low-pressure systems.
Pressure Handling Capabilities
JIC: Can handle pressures up to 10,000 psi depending on the material and size.
BSP: Generally suitable for up to 6,000 psi, but this can vary based on the material and application.
Compatibility
JIC: Primarily compatible with other JIC fittings and some SAE fittings.
BSP: Compatible with other BSP fittings and, in some cases, with Metric and NPT fittings.
Availability and Sourcing Options
JIC: Widely available in the United States and other countries that follow SAE standards.
BSP: Widely available in the UK and countries that follow British standards.
How to Identify JIC and BSP hydraulic fittings
Visual Inspection
JIC Fittings
JIC fittings are easily recognizable by the two marks present on the hex, which is the American Standard marking. Additionally, these fittings have a 37-degree flare at the end. If you’re unsure about the angle, a specialized protractor can be used to measure it accurately. This is crucial because the 37-degree flare is a defining characteristic of JIC fittings.
BSP Fittings
For BSP fittings, you’ll typically find an indentation on the hex of a fractional fitting. This is a quick way to identify BSP over other types. The fittings sit at a 30-degree angle, which is another distinguishing feature. Furthermore, the type of threads can give you more information: tapered threads indicate BSPT (British Standard Pipe Tapered), while parallel threads indicate BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel).
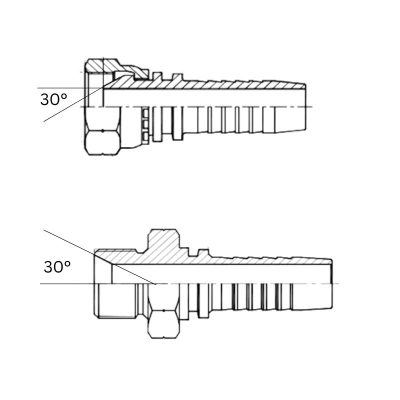
Additional Identification Methods
Thread Pitch: Use a thread gauge to measure the threads per inch (TPI) for both JIC and BSP fittings. JIC usually has a finer thread, while BSP threads are generally coarser.
Country of Origin: JIC is predominantly used in the United States, while BSP is common in the UK and other countries that follow British standards. Knowing the origin of the machinery can offer clues.
Manufacturer’s Markings: Some manufacturers include specific markings or codes on the fittings, which can be cross-referenced with product manuals for identification.
How to Measure JIC and BSP Fittings
Measuring JIC Fittings
Diameter
When it comes to measuring the diameter of JIC fittings, precision is key. Utilize calipers to measure the outer diameter of the male thread or the inner diameter of the female thread. This step is crucial for ensuring that the fitting will properly connect with its corresponding component, thereby preventing any potential leaks or system failures.
Thread Count
Thread count is another vital metric. To determine the thread pitch, count the number of threads within an inch. This information is essential for compatibility, especially when you’re dealing with high-pressure hydraulic systems where even a minor mismatch can lead to significant issues.
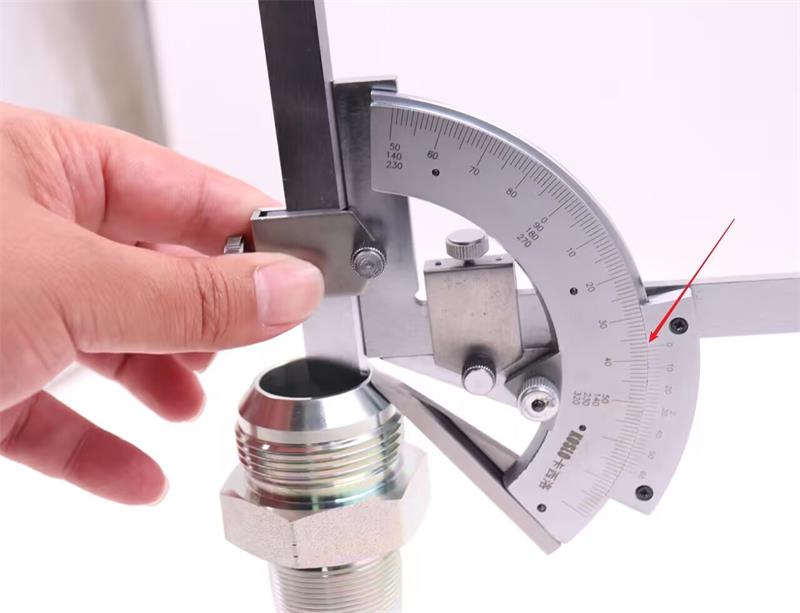
Flare Angle
The flare angle is a defining characteristic of JIC fittings. Use a specialized angle gauge to confirm the 37-degree flare angle. This is especially important in high-pressure applications where a secure, leak-proof connection is paramount.

Measuring BSP Fittings
Diameter
Just like with JIC fittings, the diameter is a critical measurement for BSP fittings. Use calipers to measure the major diameter of the male thread or the inner diameter of the female thread. Accurate measurement ensures that the fitting will seamlessly integrate into your hydraulic system.
Thread Count
BSP thread pitch is generally measured in threads per inch (TPI). To accurately determine this, use a thread gauge. Knowing the correct TPI is essential for ensuring that the BSP fitting will be compatible with other components in the system.
Thread Angle
BSP fittings have a unique 55-degree thread angle. Confirm this angle using an angle gauge to ensure you have the right type of fitting. This is particularly important in applications requiring a secure, leak-proof connection.
Type
BSP fittings come in two main types: BSPP (parallel) and BSPT (tapered). To determine which type you have, use a parallel or tapered gauge. This is crucial because each type has its own set of applications and compatibility requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business
Assessing Your Needs
Before diving into the specifics of BSP and JIC fittings, it’s crucial to assess the needs of your hydraulic systems. Consider factors like operating pressure, fluid type, temperature, and the geographical location of your operations. These elements will guide you in making an informed decision.
BSP vs JIC: A Quick Comparison
BSP (British Standard Pipe) Fittings: Known for their excellent sealing properties and global acceptance. They are versatile, with both parallel (BSPP) and tapered (BSPT) options. Ideal for high-pressure, high-vibration applications.
JIC (Joint Industry Council) Fittings: Recognized for their high-pressure handling capabilities and 37-degree flare angle. They are predominantly used in the United States and are versatile, and compatible with a wide range of tubing and hose materials.
The Right Choice for You
High-Pressure Systems: If your operations require high-pressure handling, JIC might be more suitable due to its 37-degree flare design.
Global Operations: If your business operates internationally, especially in regions following British standards, BSP fittings might be the better option due to their global acceptance.
Versatility: If you need a fitting that can be used in a variety of applications, both JIC and BSP offer versatility, but BSP provides an added advantage with its parallel and tapered options.
Cost-Effectiveness: JIC fittings are generally more expensive due to their high-pressure capabilities. If cost is a significant factor, BSP might be a more economical choice.
Choosing the Best Manufacturer
Quality Assurance: Look for manufacturers who offer quality certifications and can provide test reports for their products.
Product Range: Choose a manufacturer that offers a wide range of fittings, giving you more options to find the perfect fit for your needs.
Customer Support: Excellent customer service, including after-sales support, can be a deciding factor.
Reputation: Research customer reviews and industry reputation to ensure you’re partnering with a reliable manufacturer.
Customization: If your hydraulic systems have unique requirements, a manufacturer that offers customization services can be invaluable.
By considering these factors, you can make an informed decision that aligns with the specific needs of your business. Whether you opt for BSP or JIC fittings, the key is to choose based on your operational requirements, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Why Choose Topa
Unmatched Quality
At Topa, we pride ourselves on delivering high-quality hydraulic fittings that meet international standards. Our products undergo rigorous quality checks to ensure they meet the high-pressure and high-performance demands of hydraulic systems.
Extensive Product Range
Topa offers an extensive range of hydraulic fittings, including both BSP and JIC types. This wide selection ensures that you’ll find the perfect fit for your specific needs, whether you operate domestically or internationally.
Competitive Pricing
Being a direct factory, Topa offers competitive pricing without compromising on quality. Our products provide a higher cost-performance ratio, making us a go-to choice for businesses looking for both affordability and performance.

Exceptional Customer Service
Customer satisfaction is at the core of our business. Our dedicated customer support team is always ready to assist you with any inquiries or issues you may have, both pre-sale and post-sale.
Proven Track Record
With years of experience in the hydraulic industry, Topa has built a reputation for reliability and excellence. Our clients, who range from experienced salespeople to maintenance professionals, trust us for their hydraulic fitting needs.
By choosing Topa, you’re not just buying a product; you’re investing in a partnership that offers quality, reliability, and value. Make the right choice for your business—choose Topa, the best hydraulic fittings manufacturer in China.
Conclusion
In summary, the decision between JIC and BSP fittings boils down to your specific needs, and this guide serves as a comprehensive resource to help you navigate this complex yet crucial aspect of hydraulic systems. Choose wisely, and you’ll set the stage for operational excellence and long-term success.