An vs JIC Hydraulic Fittings: What's the Difference?
The Genesis of JIC Fittings
JIC (Joint Industrial Council) fittings originated to serve industrial applications and have become a staple in various sectors, including manufacturing and construction. The development of hydraulic systems can be traced back to the early 20th century when threaded fittings were the norm. However, these fittings are easy to leak and inefficient. By the 1930s, a new era dawned with the development of compression-style hydraulic hose fittings, providing a more secure and leak-proof seal. These were typically made from brass or steel and found applications in mining, construction, manufacturing, and transportation.
The Advent of AN Fittings
AN (Army-Navy) fittings, on the other hand, were initially designed for military applications, particularly in aerospace. During the 1950s and 1960s, as hydraulic systems became more prevalent in aerospace and defense, new materials and designs were developed. Lightweight aluminum fittings capable of withstanding high pressures and extreme temperatures were introduced. These fittings met stringent military standards like MIL-F-5509 and were used in high-stakes applications like aircraft landing gear and control systems.
Evolution Over Time
Both types of fittings have evolved significantly over the years. The 1970s and 1980s saw the development of new hydraulic hose materials like synthetic rubber and thermoplastics, leading to even more durable and resistant fittings. Today, these fittings come in a wide range of materials, sizes, and configurations to meet industry-specific needs.
JIC Fittings
JIC (Joint Industry Council) fittings are flare-type connectors designed for high-pressure applications. They are an integral part of hydraulic systems, fuel delivery mechanisms, and other fluid power applications. These fittings are especially useful in systems that require pressure levels up to 10,000 PSI.
Appearance and Characteristics
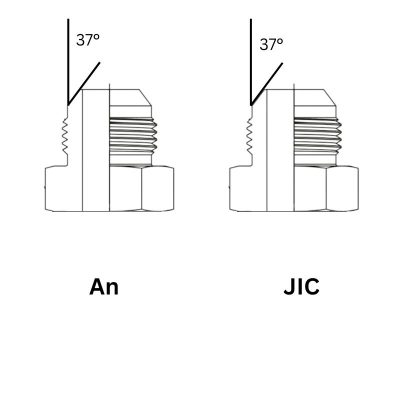
JIC fittings are typically made of forged carbon steel, although other materials like stainless steel, brass, and nickel-copper alloys are also used. They feature a 37-degree flare seating surface, which ensures a secure and leak-proof connection. The fittings come in various sizes and configurations, including straight, elbow, and tee shapes, among others.
International Standards

These fittings adhere to international standards such as SAE J514 and MIL-DTL-18866. The SAE J514 standard has effectively replaced the older MS16142 military specification, although some tooling still references the older code. These standards ensure that the fittings meet quality and dimensional requirements, making them reliable choices for industrial applications.
Advantages
Durability: One of the most significant advantages of JIC fittings is their rugged construction. Made from high-quality materials such as forged carbon steel or stainless steel, these fittings can withstand high pressures. They can withstand harsh environments such as extreme temperatures and corrosive substances, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Versatility: JIC fittings are not limited to a single application or industry. They are used in a wide range of applications, from hydraulics and fuel delivery mechanisms to fluid power applications in industrial environments. This versatility means you can use standardized JIC fittings in multiple systems.
Standardized: JIC fittings conform to international standards such as SAE J514 to meet stringent quality and dimensional requirements. This standardization is critical for interchangeability, allowing you to easily swap out parts from different manufacturers without worrying about compatibility issues.
Cost Effective: JIC fittings are cost-effective considering their durability and versatility. They offer long-term value, reducing the need for frequent replacement.
Disadvantages
Specialized Tools: One of the drawbacks is that specialized tools may be required to install JIC fittings. These tools can add to the initial installation cost.
Tolerance Levels: JIC fittings have less stringent tolerance requirements than AN (Army-Navy) fittings. While this is not usually a problem for most industrial applications. However, in highly specialized systems, even the slightest variation can affect performance.
Possibility of over-tightening: Due to their flared design, there is a risk of over-tightening, which can deform the fitting and lead to leaks. Proper training is required to ensure proper fitting installation.
Not Suitable for Dynamic Stress: While JIC fittings are well suited for high-pressure applications, they may not be the best choice for dynamically stressed systems, such as frequent vibration or thermal cycling.

Applications
Construction and Manufacturing Equipment
JIC fittings are commonly found in hydraulic systems that power heavy machinery such as excavators, bulldozers and cranes. Their rugged design ensures they can withstand the high pressures and harsh conditions often encountered on construction sites. In manufacturing environments, they are used in hydraulic presses, conveyor systems, and automated machinery for reliable performance and minimal downtime.
Automotive and Marine Applications
In the automotive industry, JIC fittings exist in fuel delivery systems, including fuel lines and fuel injection systems. Their durability and high-pressure tolerance make them ideal for the harsh conditions of modern engines. In marine applications, JIC fittings are used in the fuel systems of boats and ships, which must not only withstand high pressures but also corrosive saltwater environments.
Industrial Machinery
JIC fittings are also used in a variety of fluid power applications in industrial environments. These include hydraulic systems in manufacturing plants, pneumatic controls in automation, and lubrication systems in heavy machinery. Their standardization and versatility make them a popular choice for engineers and maintenance professionals.
Renewable Energy Systems
As the world moves toward more sustainable energy solutions, renewable energy systems such as wind turbines and solar panel trackers are frequently utilizing JIC hydraulic fittings.
Medical Equipment
In special cases, JIC fittings exist in medical equipment such as patient hydraulic lifts and specialized surgical tools. In these life-sustaining applications, their reliability and adherence to standards is critical.
AN fittings
Originally designed for the U.S. Army, AN (Army-Navy) joints are known for their ruggedness and durability. Developed during World War II, these fittings were the product of fitting standards agreed upon by the Army Air Corps and the Navy. Over the years, their applications have expanded beyond the military, especially in high performance systems.
Appearance and Characteristics
Appearance and Features
At first glance, AN fittings may look similar to JIC fittings, but they are typically made of higher quality materials. These fittings typically consist of lightweight aluminum, stainless steel, or titanium, and feature a 37-degree flared seating surface. The premium materials used in AN fittings allow them to withstand extreme conditions, including high pressure and high temperature.
International Standards

International Standards
AN fittings meet military specifications such as MIL-F-5509 and are currently governed by SAE aerospace standards (AS4841 through AS4843 and AS4875). These standards ensure that fittings meet the stringent requirements of aerospace and military applications.
Advantages
High-quality: AN fittings are made from high-quality materials such as aluminum, stainless steel, and titanium. This ensures not only product longevity but also unmatched reliability, especially in high-risk environments.
Precision: AN fittings are manufactured to exacting military and aerospace standards with precise tolerances. This precision makes them the preferred choice for specialized applications where even small deviations can have serious consequences.
High-Pressure Tolerance: These fittings can withstand extreme conditions, including high pressure and high temperature.
Corrosion-resistance: Due to the use of high-quality materials, AN fittings have excellent corrosion resistance, making them suitable for marine and other corrosive environments.
Disadvantages
High Cost: The flip side of high-quality materials and manufacturing standards is cost. AN fittings are typically more expensive than JIC fittings because of the materials used, among other things.
Limited Interchangeability: Although AN fittings look similar to JIC fittings, they are not universally interchangeable due to their specific tolerances and materials. This can complicate matters when trying to integrate them into existing systems.
Availability: Because of their specificity, AN fittings may not be as readily available as more standard types, so purchases need to be planned in advance.
Installation complexity: The precision of AN fittings often requires specialized tools and expertise for installation, adding time and cost to the overall project.

Applications
Aerospace
AN fittings are a staple in the aerospace industry and exist in critical hydraulic systems in aircraft, including landing gear, flight control systems, and fuel delivery.
High Performance Vehicles
AN fittings are standard in motorsports and high-performance vehicles. Their reliability and performance make them ideal for fuel, cooling, and hydraulic systems in race cars and luxury automobiles.
Military Equipment
From tanks and armored vehicles to warships and aircraft, AN fittings serve a wide variety of military applications where failure is not an option.
Specialty Industries
Medical equipment: In specialized medical facilities, AN couplings serve in medical equipment such as hydraulic patient lifts and surgical tools. In such equipment, high precision and reliability are essential.
Chemical and pharmaceutical industries: AN fittings are corrosion-resistant and made of high-quality materials. Therefore, they are also used in chemical processing plants and the pharmaceutical industry to handle the transfer of sensitive or corrosive substances.
Differences Between JIC and AN Fittings
Connector Markings
AN Fittings: These often come with identifiable markings, usually indicating the manufacturer, material, and military or aerospace standards met. These markings provide an added layer of assurance regarding the fitting’s quality and origin.
JIC Fittings: While they may also have markings, these are usually less comprehensive and may only indicate size or basic material information.
Thread Size and Dimensions
AN Fittings: Manufactured to exacting tolerances, the thread size and dimensions are highly consistent, adhering to strict military and aerospace standards.
JIC Fittings: While similar in size, they are produced to industrial standards, which are generally less stringent. This means they may not always be interchangeable with AN fittings.
AN/JIC FITTING & TUBE INFORMATION | |||||
DASH S1ZE | BRAIDED | HARD TUBE | AN/JIC | AN FLARE | AN/JIC WIRE |
-3 | 1/8″ | 3/16″ | 3/8″ x24 | 0.125″ | 7/6″ or 12″ |
-4 | 7/32″ | 1/4″ | 7/16″x20 | 0.171″ | 9/16″ |
-6 | 11/32″ | 3/8″ | 9/16″x18 | 0.298″ | 11/16″ |
-8 | 7/16″ | 1/2″ | 3/4″x16 | 0.391″ | 7/8″ |
-10 | 9/16 | 5/8″ | 7/8″x14 | 0.484″ | 1″ |
-12 | 11/16″ | 3/4″ | 1-1/16″x12 | 0.608″ | 1-1/4″ |
-16 | 7/8″ | 1″ | 1-5/16″x12 | 0.844″ | 1-1/2″ |
-20 | 1-1/8″ | 1-1/4″ | 1-5/8″x12 | 1.078″ | 1-13/16″ |
Flare Angle and Sealing Mechanism
Both Types: Both JIC and AN fittings feature a 37-degree flare seating surface.
Differences: The tolerances may differ, with AN fittings often having tighter tolerances due to their military-grade requirements. This can affect the sealing mechanism and the ability to form a leak-proof connection.
Pressure Rating Ranges
AN Fittings: These are often rated for higher pressures, making them suitable for critical applications like aerospace and military equipment.
JIC Fittings: While also designed for high-pressure systems, they may not meet the extreme pressure requirements of specialized applications.
Materials and Compatibility
AN Fittings: Typically made from higher-grade materials like lightweight aluminum, stainless steel, or titanium, making them more suitable for specialized applications where material compatibility is crucial.
JIC Fittings: Commonly made from forged carbon steel, although other materials like stainless steel and brass are also used. These are generally more cost-effective but may not offer the same level of material compatibility as AN fittings.
Are JIC and AN fittings interchangeable?
Whether or not JIC and AN fittings are interchangeable is a common question, especially considering their similar appearance and 37-degree flare angle. However, the international recommendation is not to interchange JIC and An fittings.
Why not
Critical Systems: In high-stakes environments like aerospace, military, or medical applications, it’s advisable not to interchange JIC and AN fittings due to the stringent standards and tight tolerances required.
Different Materials: If the fittings are made from different materials, interchanging them could lead to compatibility issues, such as galvanic corrosion.
Tolerance Levels: AN fittings are manufactured to more exact tolerances than JIC fittings. Interchanging them in a system that requires high precision could lead to leaks or system failure.
Certification Requirements: In systems that must meet specific certifications, like military or aerospace standards, interchanging fittings that don’t meet those standards could result in non-compliance.
Risks of Incorrect Interchangeability
System Failure: Using the wrong fitting in a critical system could lead to catastrophic failure, posing safety risks.
Increased Maintenance: Incorrect interchangeability could result in leaks or other issues, leading to increased maintenance costs and downtime.
Voided Warranties: Using non-approved fittings could void the warranty of the hydraulic system or the equipment in which it is installed.
How to Choose the Right JIC and AN Fitting
Selecting the appropriate JIC or AN fitting for your hydraulic system is a critical decision that can impact the system’s performance, safety, and longevity. Here are some key factors to consider:
Environmental Factors and Industry Requirements
Operating Environment: Consider the conditions where the hydraulic system will operate. This includes temperature ranges, exposure to corrosive substances, and potential for mechanical impact.
Compliance Needs: Different industries have varying standards and certifications. Make sure the fittings you choose meet or exceed these requirements, especially for critical applications like aerospace or healthcare.
Hydraulic System Compatibility
Pressure Requirements: Ensure that the fitting can withstand the system’s maximum operating pressure. AN fittings are generally suitable for higher-pressure applications, while JIC fittings are often used in industrial settings.
Flow Requirements: The fitting should be sized appropriately to match the system’s flow rate. Incorrect sizing can lead to inefficiencies or system failure.
Availability and Sourcing
Lead Time: Consider the availability and lead time for the fittings, especially for large projects or critical applications where downtime is costly.
Quality Assurance: Look for suppliers who offer quality certifications and testing to ensure the fittings meet your standards.
Where to Buy
Local Suppliers: Local suppliers may offer quick delivery but may have higher prices or limited selection.
Online Retailers: These offer a wide range of options but may lack personalized customer service.
Direct from Manufacturers: Purchasing directly from manufacturers can offer a high cost-performance ratio. You get high-quality products at competitive prices, backed by expert advice.
Why Choose Topa Hydraulic?
Quality: Topa Hydraulic fittings meet or exceed industry standards, ensuring reliability and performance.
Cost-Performance Ratio: Manufactured in China, our products offer a high cost-performance ratio, providing quality at an affordable price.
One-Stop Service: From consultation to delivery, Topa Hydraulic offers a seamless customer experience, saving you time and effort.
Conclusion
By taking a comprehensive approach to selecting hydraulic fittings, you not only ensure the optimal performance of your system but also contribute to its long-term reliability and safety. For those looking to make an informed choice, Topa offers a wide range of JIC and AN fittings that meet stringent industry standards, providing you with options that can be tailored to your specific needs. Would you like to explore these options further? Feel free to reach out to us for any inquiries or assistance you may require.











































