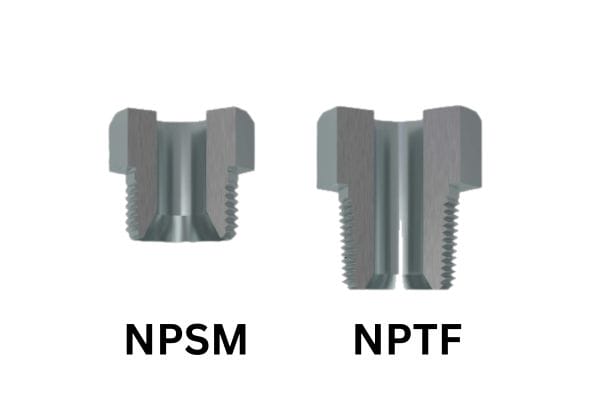
Understanding the types of threads used in pipes and fittings is crucial for ensuring the efficiency, safety, and reliability of hydraulic and plumbing systems. NPSM threads, also known as National Pipe Straight Mechanical threads, are particularly essential in these industries because they offer a unique approach to pipe fitting that differs from the more common tapered threads like NPT (National Pipe Tapered).
What Are NPSM Threads?
Definition
NPSM (National Pipe Straight Mechanical) threads are a type of pipe thread used primarily in hydraulic and plumbing applications. Unlike other thread types that may be tapered, NPSM threads are designed as straight threads, meaning they maintain a consistent diameter along their entire length. This standardization is defined by the ANSI (American National Standards Institute) and focuses on mechanical connections rather than creating pressure-tight seals. The purpose of NPSM threads is to provide a secure fit that relies on additional sealing components, such as O-rings or gaskets when needed to prevent leaks.
Thread Characteristics
Straight (Non-Tapered) Nature: NPSM threads are parallel, meaning they do not taper inward or outward along the length of the thread. This is in contrast to NPT (National Pipe Tapered) threads, which gradually narrow, creating a wedging effect when tightened.
Mechanical Functionality: Since NPSM threads do not taper, they are primarily designed for mechanical connections rather than for sealing on their own. They are ideal for applications where a tight mechanical fit is necessary, and the seal is achieved using additional components like sealing washers or O-rings.
Compatibility with NPTF Threads: NPSM threads are often compatible with NPTF (National Pipe Tapered Fuel) threads. While NPSM threads themselves are not tapered, they can work with NPTF counterparts, which are specifically designed to create a dry seal. This compatibility allows NPSM and NPTF components to be used together, particularly when a non-leak seal is necessary for hydraulic or pneumatic systems.

Comparison with NPT Threads
Tapered vs. Straight Design: The primary distinction between NPSM and NPT threads lies in their structure. NPT threads are tapered, meaning they decrease in diameter as they extend, creating a tight, wedging seal when two NPT components are threaded together. This self-sealing characteristic makes NPT threads suitable for pressure-tight applications, often eliminating the need for additional sealing components.
Application Differences: NPSM threads, being straight, do not create this pressure-tight seal on their own. Therefore, they are used in situations where the primary requirement is mechanical strength rather than sealing capability. NPT threads are commonly used for high-pressure systems where a reliable, leak-proof connection is essential without additional seals.
Sealing Mechanics: In NPT systems, the taper creates a metal-to-metal seal as the threads compress against one another. In contrast, NPSM threads depend on supplementary components like O-rings or washers to ensure a leak-free connection. This makes NPSM threads advantageous for applications where maintaining a consistent diameter is important, and flexibility in sealing options is required.
History and Development of NPSM Threads
Origins
NPSM threads originated in the early 20th century as industries began to standardize various pipe threading practices in North America. As the demand for reliable and efficient connections in hydraulic, plumbing, and mechanical systems grew, it became clear that a consistent and standardized thread type was needed to ensure compatibility across different manufacturers and applications. The introduction of NPSM threads filled this gap by providing a non-tapered, straight thread option that could be used in various mechanical applications without the need for a self-sealing mechanism.
Development
The evolution of pipe threading standards has been heavily influenced by organizations such as the ANSI (American National Standards Institute). ANSI played a pivotal role in establishing guidelines for various types of threaded connections, including NPSM. In the mid-20th century, as industrial standards began to be more formalized, ANSI developed specifications that outlined the dimensions, tolerances, and performance requirements for NPSM threads. This standardization was crucial for manufacturers and engineers, allowing for interchangeable components that could ensure safety and performance across different systems and applications.
Why NPSM Threads Were Created
NPSM threads were created to address specific challenges associated with traditional tapered threads, particularly in applications where a mechanical fit was necessary without the complexities of a sealing system. The straight design of NPSM threads allows for easier alignment and assembly, making them ideal for scenarios where components must fit together without altering their structural integrity.
Moreover, NPSM threads provide flexibility by allowing users to select appropriate sealing materials based on their specific application needs. This adaptability makes NPSM threads suitable for various industries, including hydraulic systems and plumbing, where different environmental conditions and pressures must be accounted for. The ability to use NPSM threads in conjunction with other sealing mechanisms enhances their usability, ensuring a reliable connection while maintaining the mechanical advantages of a straight thread design.
Technical Specifications of NPSM Threads
Thread Dimensions
NPSM (National Pipe Straight Mechanical) threads are designed according to specific dimensional standards to ensure consistency and compatibility. The key dimensions for NPSM threads include:
Pitch: The pitch of an NPSM thread refers to the distance between adjacent thread peaks. NPSM threads maintain a uniform pitch that matches industry standards to ensure compatibility with other components. For example, an NPSM thread with a ½-inch diameter will have a corresponding pitch that aligns with ANSI standards.
Diameter: NPSM threads are straight, meaning they maintain a consistent outside diameter along the length of the thread. This outside diameter is crucial for ensuring that the thread fits precisely into the corresponding female fitting without tapering. The inside diameter, or root diameter, is also consistent to maintain uniformity.
Thread Angle: NPSM threads have a standard thread angle of 60 degrees, similar to other pipe threads like NPT (National Pipe Tapered). This angle ensures that the threads interlock properly when mated with compatible fittings, providing a secure mechanical connection.
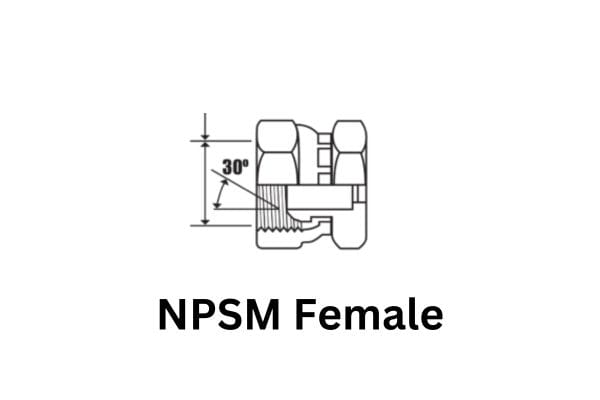
Thread Tolerance Classes
NPSM threads adhere to specific tolerance classes that determine the allowable variance in thread dimensions. Tolerances are crucial for ensuring a reliable and secure fit between male and female components. The standard tolerance classes for NPSM threads are defined by ANSI and include:
Class 2A (External Threads): This class allows for a moderate level of tolerance, suitable for general-purpose applications where components must fit together without excessive tightness. It ensures that the external threads of the male fitting will mate easily with the internal threads of the female fitting, facilitating straightforward assembly.
Class 2B (Internal Threads): This class applies to the internal threads in the female fitting. It allows for similar levels of tolerance as Class 2A, ensuring that the threads are not too tight or too loose, providing a balanced fit that can accommodate slight variations while maintaining functionality.
These tolerance classes help ensure that NPSM threads achieve the required balance between ease of installation and reliability in the fit, minimizing the risk of thread damage or poor alignment during assembly.
Standard Sizes
NPSM threads come in a variety of standard sizes, accommodating different applications and system requirements. The most common sizes include:
¼ inch NPSM: Often used in smaller hydraulic fittings, instrumentation, or low-pressure applications where precision and compact size are required.
½ inch NPSM: A common size for plumbing applications, as well as hydraulic systems, where a moderate flow rate and connection stability are necessary.
¾ inch NPSM: Typically used in larger systems requiring stronger mechanical connections, such as high-flow plumbing or certain hydraulic applications.
1 inch and above: For larger-scale systems and industrial applications, where the connection must handle greater flow rates or mechanical stress.
Each size corresponds to a specific set of dimensional and pitch standards, ensuring that components can be easily matched and interchanged within and across systems. The use of these standardized sizes allows for broad compatibility, making it easier to source and replace parts in various applications.
Limitations and Considerations
Pressure Limitations
One of the primary limitations of NPSM (National Pipe Straight Mechanical) threads is their performance in high-pressure environments. Due to their straight (non-tapered) design, NPSM threads do not create a pressure-tight seal on their own. Unlike tapered threads like NPT (National Pipe Tapered), which wedge together as they are tightened, creating a seal that can withstand higher pressure, NPSM threads rely solely on mechanical engagement without this wedging effect. As a result:
Pressure Restrictions: NPSM threads are generally limited to low- and medium-pressure applications where the mechanical strength of the connection is sufficient, but a pressure-tight seal is not critical. In hydraulic or pneumatic systems operating under higher pressures, using NPSM threads without additional sealing measures can lead to leaks or even system failure.
Sealing Requirements
Given their non-sealing nature, NPSM threads often require the use of additional sealing components, especially in applications where maintaining pressure integrity is critical. The most common sealing methods include:
O-rings: These are commonly used with NPSM fittings to create a seal between the male and female components. The O-ring sits in a groove, compressing as the threads are tightened to form a pressure-tight barrier. This method is especially effective in hydraulic systems, where reliable sealing is essential to prevent leaks.
Sealants (e.g., PTFE/Teflon Tape or Pipe Dope): For some applications, sealants may be applied to NPSM threads to enhance the connection’s leak resistance. However, this approach is generally supplementary, as the primary seal still relies on the use of an O-ring or gasket.
Gaskets: These flat sealing components can be used with NPSM threads when two flat surfaces need to be joined, providing a secure seal when compressed.
These additional sealing measures are necessary because, without them, NPSM threads alone cannot maintain a leak-free connection in high-pressure or fluid-handling systems. Engineers must ensure that the appropriate sealing method is chosen based on the system’s requirements to prevent fluid or gas escape.
Temperature Tolerance
While NPSM threads can be used across a broad range of temperatures, their performance is also influenced by the sealing components used:
Temperature Limits of NPSM Threads: The metal used for NPSM fittings (commonly stainless steel or brass) can generally handle temperatures ranging from -65°F to 400°F (-54°C to 204°C) or more, depending on the material. However, this capability depends heavily on the specific sealing materials integrated with the threads.
O-Ring and Sealant Temperature Ratings: The effectiveness of O-rings, gaskets, and sealants diminishes outside of their temperature tolerance range. For instance, standard rubber O-rings may fail at high temperatures or become brittle at very low temperatures, compromising the seal. In such cases, specialized high-temperature O-rings (e.g., made from Viton or silicone) are needed.
Alternative Thread Types: For extreme temperature applications (either very high or low), alternative thread types like NPT or NPTF (which provide a dry seal without reliance on additional materials) may be preferred, especially when sealing integrity is vital, and the environmental conditions are harsh.
How to Identify and Measure NPSM Threads
Identification Tips
Identifying NPSM threads accurately is crucial for ensuring compatibility in mechanical systems. Here are some visual and measurement techniques:
Visual Inspection: NPSM threads appear straight and parallel, lacking the taper seen in NPT threads. Look for a consistent diameter throughout the length of the threaded section.
Thread Count: Count the number of threads per inch (TPI). NPSM threads typically have a specific TPI that aligns with their size, which can help differentiate them from other thread types.
End Shape: Examine the end of the threaded fitting; NPSM threads often have a more rounded profile at the tip compared to NPT threads, which may have sharper, more defined edges.
Thread Gauges
Using thread gauges is a reliable method for measuring thread pitch and diameter:
Thread Pitch Gauge: This tool has multiple blades that allow you to measure the pitch by matching the thread profile. Align the gauge with the threads to determine the correct TPI.
Caliper: A caliper can be used to measure the external diameter of the threaded section. For NPSM, ensure the measurement is consistent along the entire length, confirming the non-tapered design.
Go/No-Go Gauges: These are specialized tools designed to quickly assess whether a thread fits within specified tolerances. A “go” gauge should fit snugly, while a “no-go” gauge should not fit at all, indicating whether the threads are within acceptable limits.
Common Mistakes in Identification
When identifying NPSM threads, several common errors can occur:
Confusing NPSM with NPT: The most frequent mistake is mistaking NPSM for NPT threads due to their similar appearance. To avoid this, always check for taper; if the threads are straight, they are NPSM.
Ignoring Thread Count: Failing to measure the TPI can lead to incorrect identification. Always confirm the thread count against standard specifications for NPSM.
Neglecting Compatibility: Even if NPSM and NPT threads appear similar, they may not be compatible in practice. Ensure that any mating components are designed for the same thread type to avoid leaks or failures.
NPSM vs. Other Thread Types
NPSM vs. NPT
Sealing Mechanics: NPT threads create a seal through their tapered design, which compresses against the male fitting to form a tight, pressure-resistant barrier. NPSM threads, on the other hand, do not provide this self-sealing feature and rely on additional sealing components, like O-rings.
Applications: NPT threads are used in applications where a leak-proof connection is critical, such as high-pressure systems. NPSM threads are suitable for mechanical connections where flexibility in sealing methods is desired.
Pressure Tolerance: NPT threads can generally handle higher pressures due to their self-sealing properties. NPSM threads are limited to lower pressures unless supplemented with effective sealing materials.
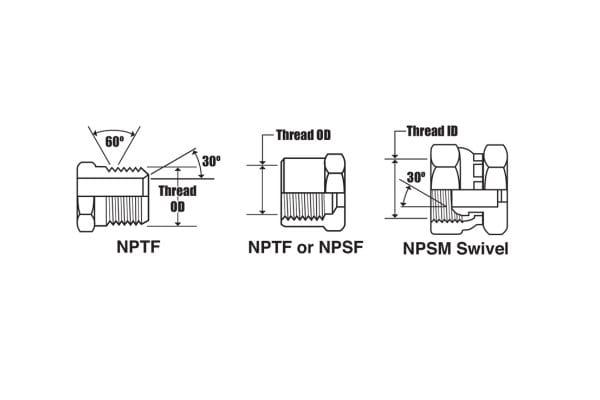
NPSM vs. BSPP (British Standard Pipe Parallel)
Compatibility: NPSM threads are predominantly used in North America, while BSPP threads are more common in European and Commonwealth countries. Although both are straight threads, they have different dimensions and tolerances, making them incompatible without appropriate adapters.
Geographic Usage: The choice between NPSM and BSPP often depends on regional standards and the specific industry. For example, plumbing components in North America will typically use NPSM, while those in the UK may use BSPP.
NPSM vs. NPTF (Dryseal)
Usage Together: NPSM threads can be used with NPTF threads, as they both share similar diameters and are designed for mechanical strength. However, while NPTF threads provide a dry seal without the need for additional sealing materials, NPSM threads require supplementary components to ensure leak resistance.
Importance of Sealing Techniques: When combining NPSM and NPTF components, it’s essential to ensure proper sealing techniques are used. For instance, O-rings should be correctly placed to accommodate the straight nature of NPSM threads, while NPTF threads can create a seal without relying solely on additional sealing materials.
Conclusion
For professionals in hydraulic, plumbing, and related fields, it is crucial to remember that NPSM threads provide reliable mechanical connections but require additional sealing components for effective performance in high-pressure situations. Understanding how to identify and measure NPSM threads accurately will help ensure compatibility with other components, reducing the risk of leaks and enhancing system reliability. Familiarity with the differences between NPSM and other thread types will facilitate better decision-making when selecting fittings for various applications.
FAQ
What does NPSM stand for?
NPSM stands for National Pipe Straight Mechanical, which refers to a standard for straight pipe threads used in various mechanical applications.
How do NPSM threads differ from NPT threads?
NPSM threads are straight and do not create a self-sealing effect, while NPT (National Pipe Tapered) threads are tapered and form a seal through compression as they are tightened.
What applications are suitable for NPSM threads?
NPSM threads are commonly used in plumbing and hydraulic systems, particularly where mechanical connections are needed without the requirement for a pressure-tight seal.
Do NPSM threads require additional sealing materials?
Yes, NPSM threads typically require additional sealing components, such as O-rings or sealants, to ensure leak resistance, especially in high-pressure applications.
What are the standard sizes available for NPSM threads?
Common standard sizes for NPSM threads include ¼ inch, ½ inch, and ¾ inch, among others, each used for different applications based on flow rates and mechanical requirements.
How can I identify NPSM threads?
To identify NPSM threads, look for straight, parallel threads and measure the pitch and diameter. Using thread gauges can help ensure accurate identification.