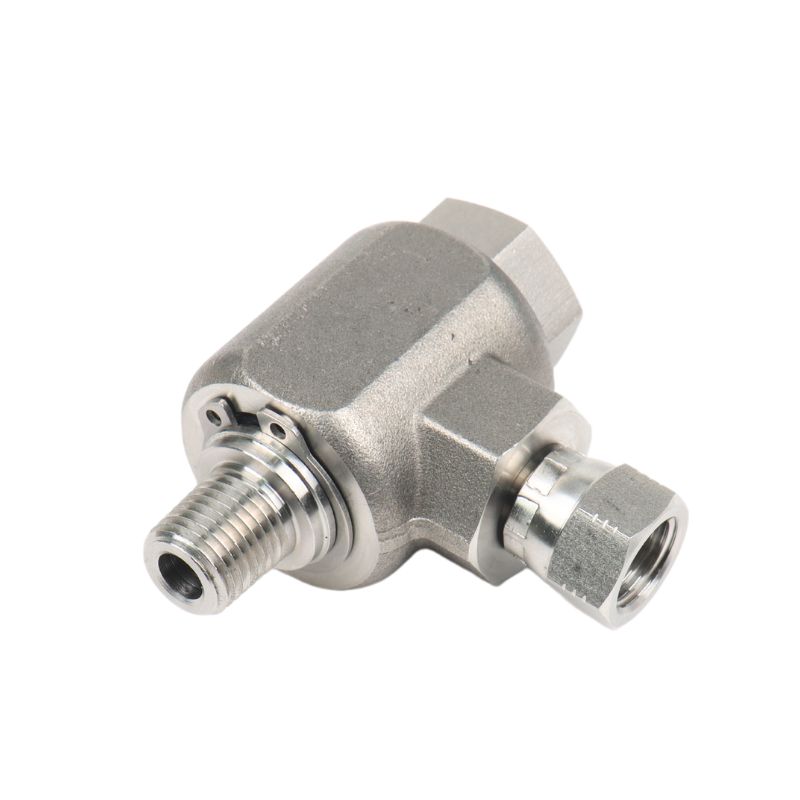
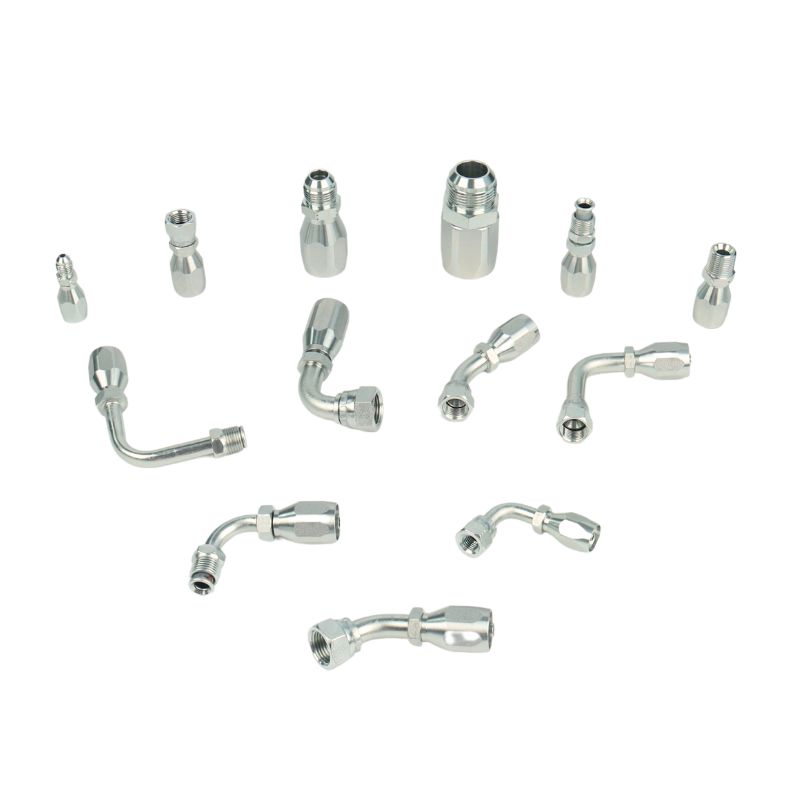
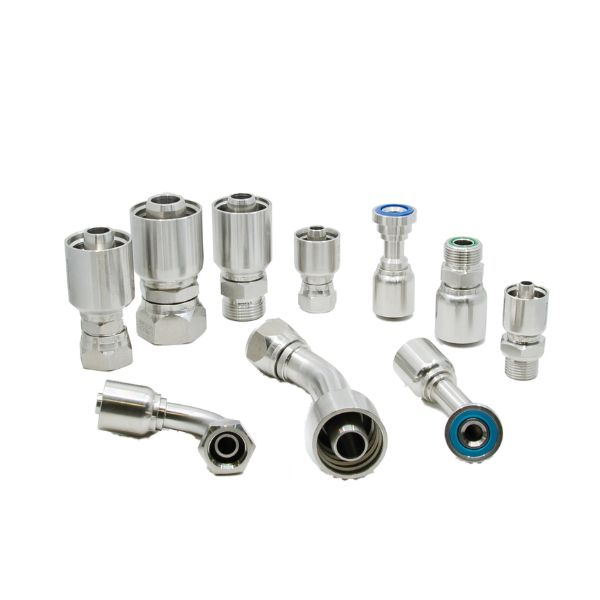
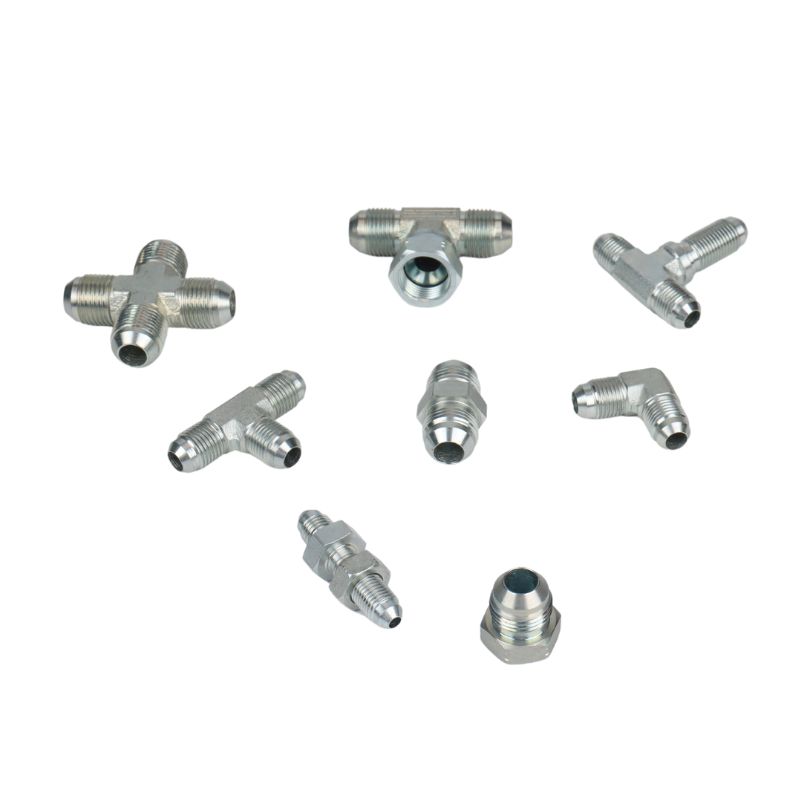
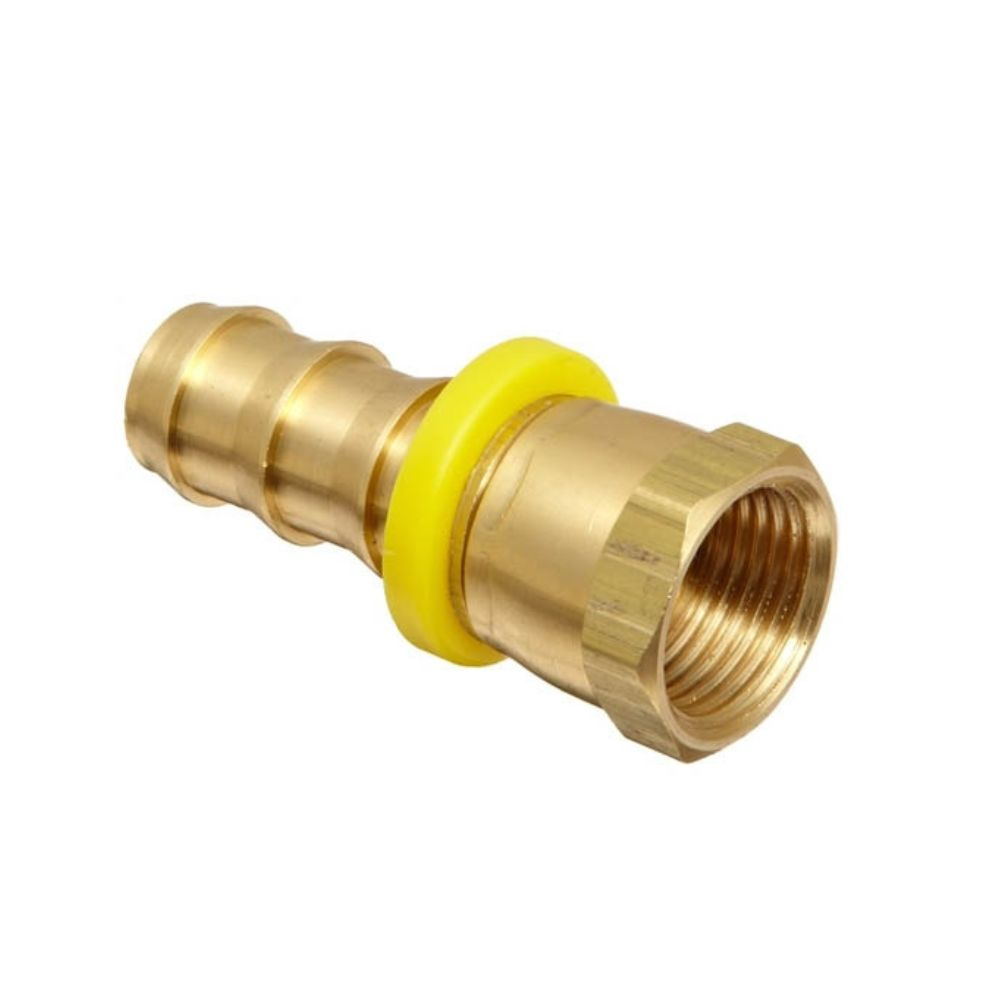
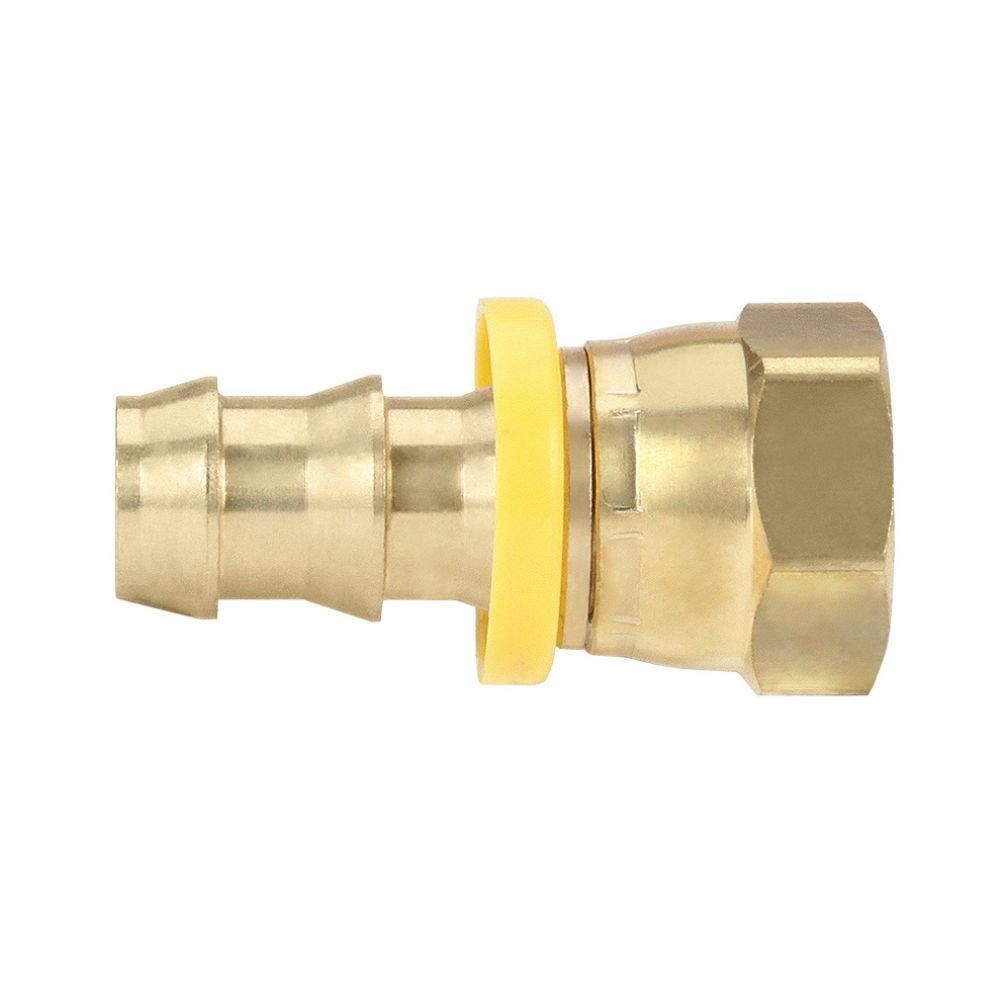
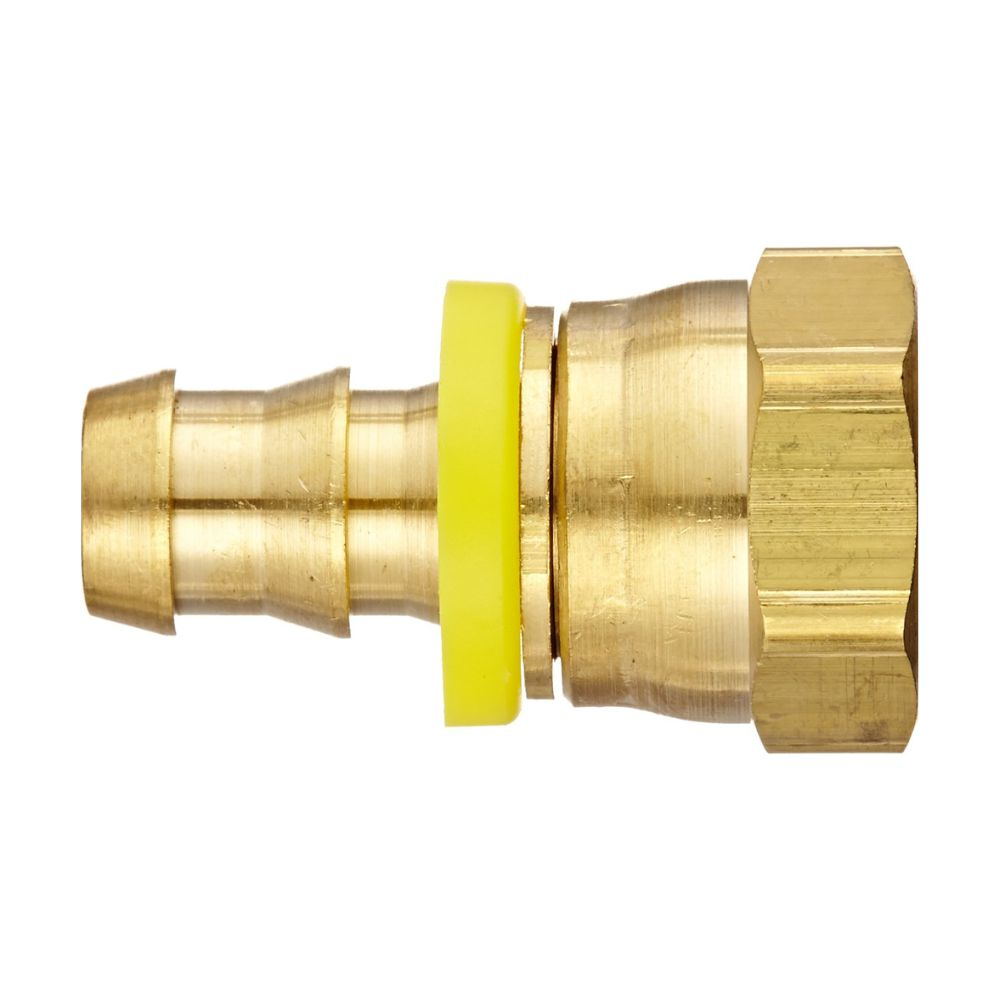
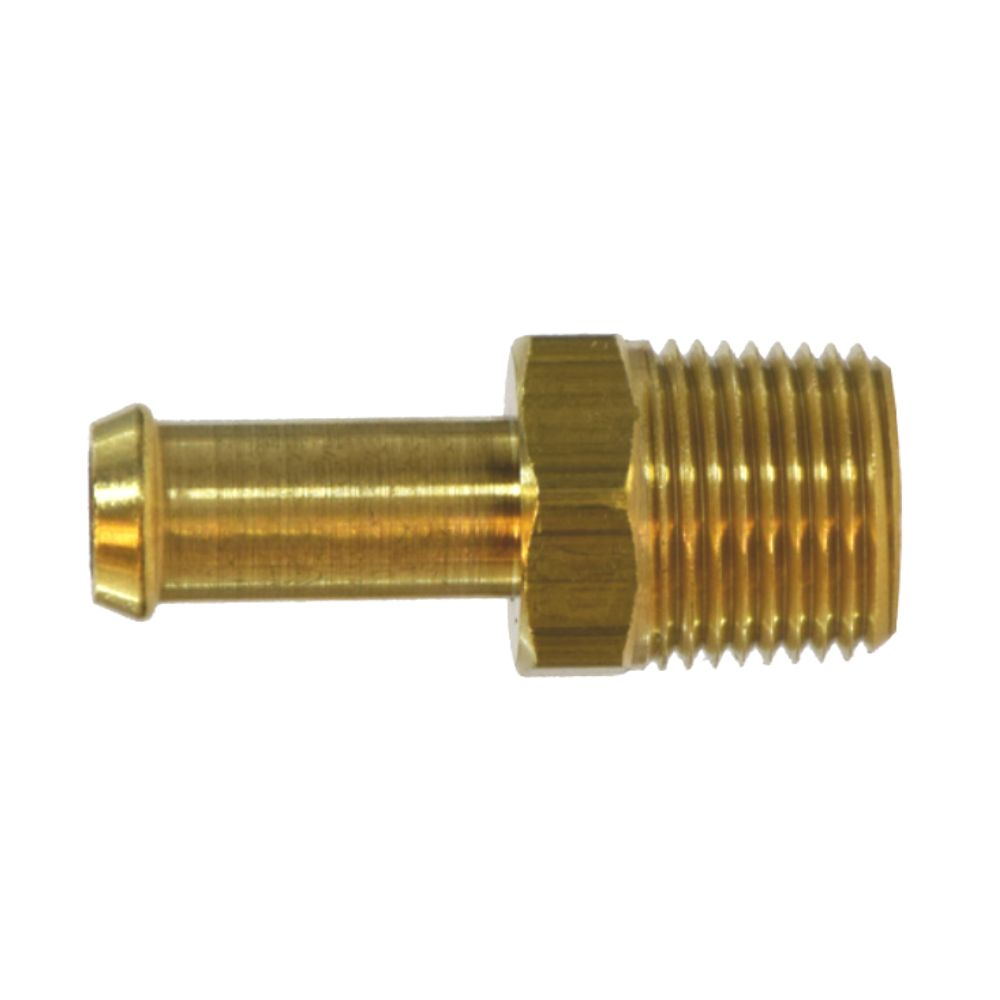
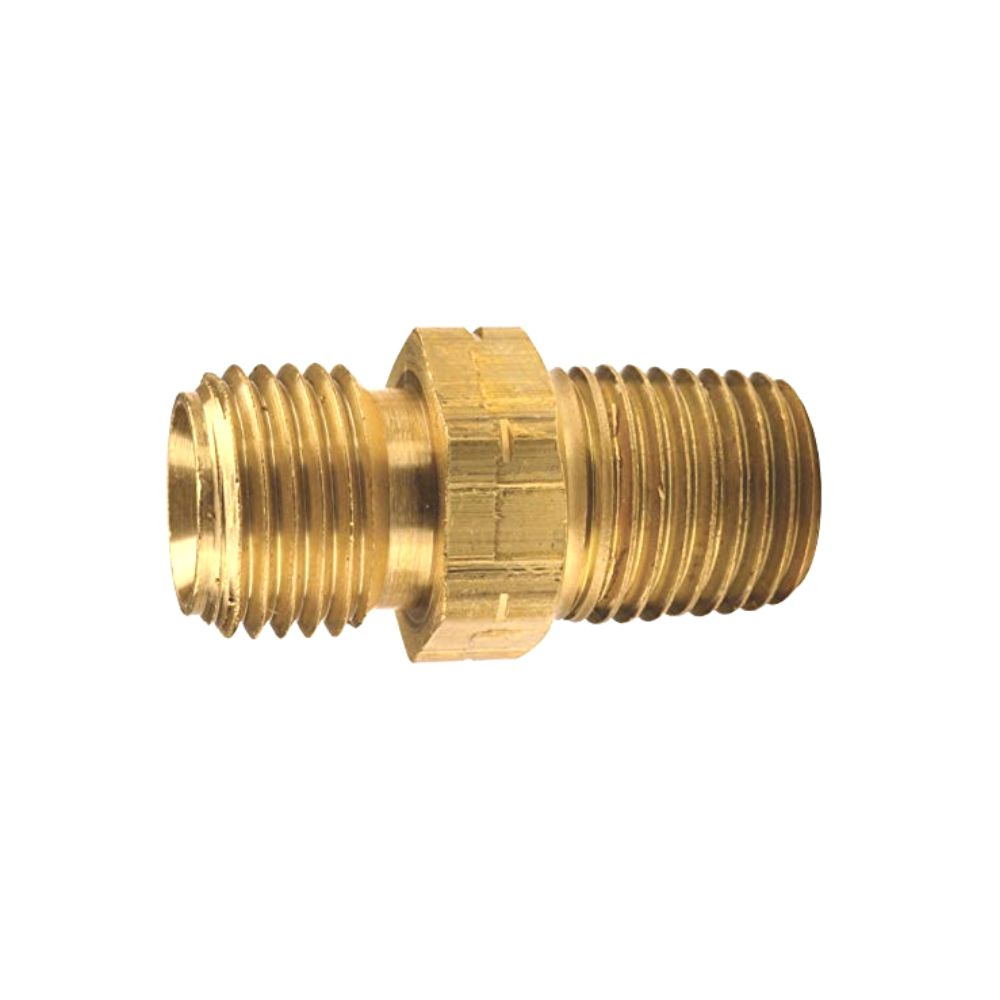
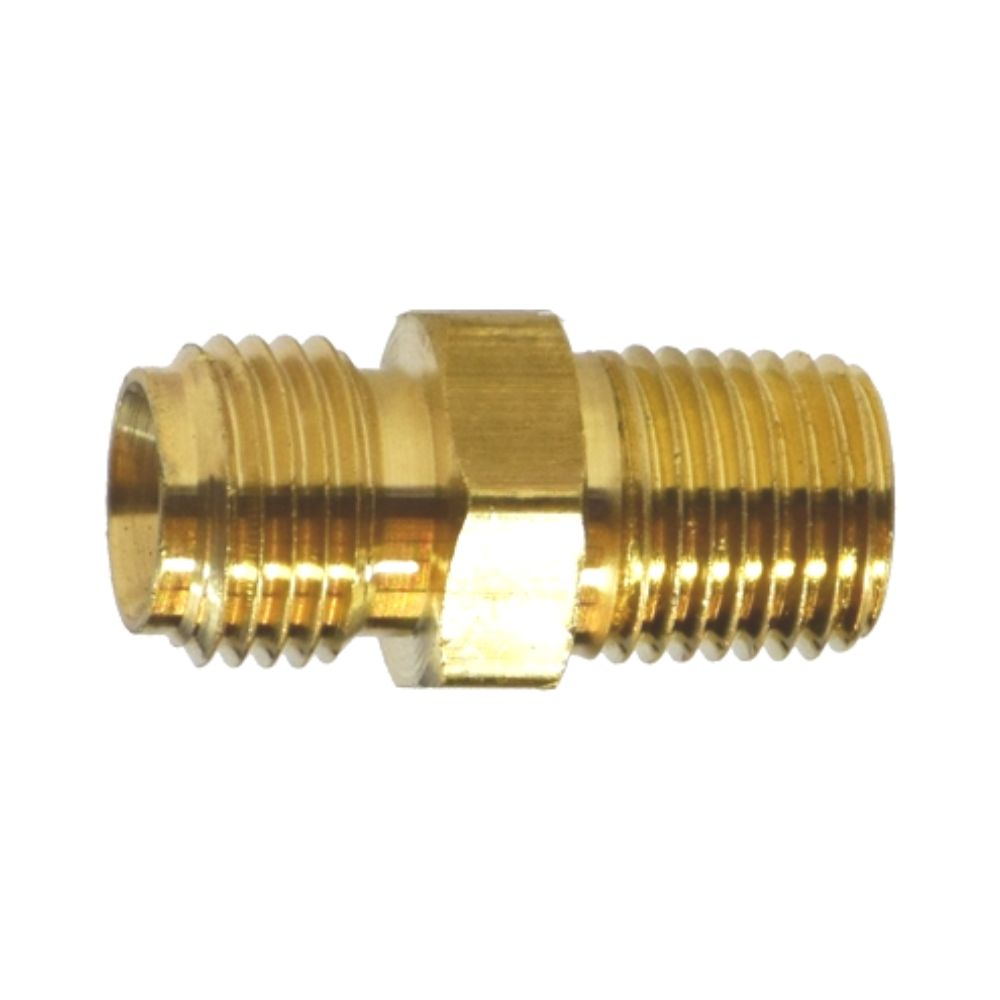
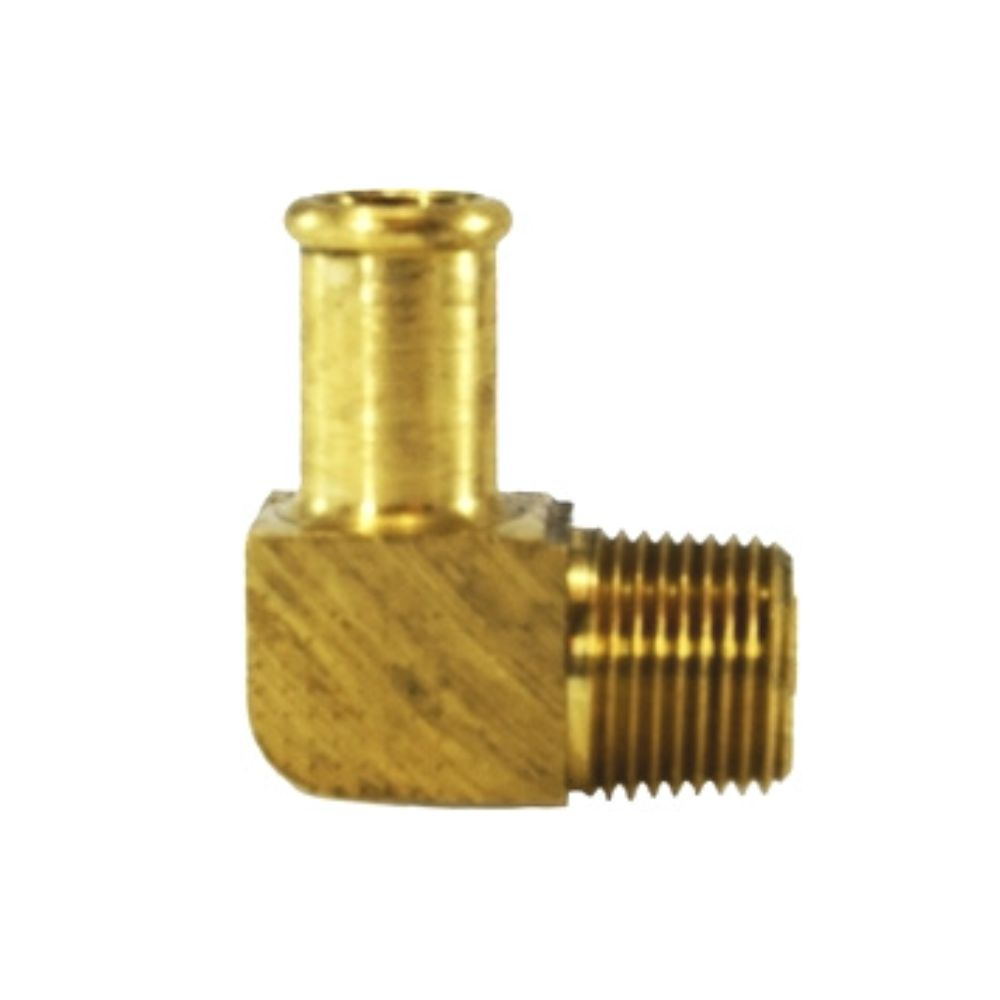
Best China Hydraulic Swivel Fittings Manufacturer
❖ Suitable for narrow spaces
❖ Withstand high pressure
❖ Adopt pressure balance design
❖ The maximum speed is 10 rpm
Best China Hydraulic Swivel Fittings Supplier
Hydraulic live swivel fittings, often referred to as hydraulic live swivels, are a more specialized type of hydraulic fitting. These fittings are designed with bolts, o-rings, and hydraulic fittings, and the fittings are threaded on both ends to connect with different equipment. Their unique 90 degree bend design prevents twisting and torque on the hose caused by mechanical movement.Topa can supply all swivel fittings, if you have a need or question, please contact us!
Product List
Hydraulic swivel fittings are available in a wide range of threads, such as BSP, JIC, Metric, NPT, and SAE, and we have the right size and material for you. Moreover, if you need special threads or sizes of fittings, you can contact Topa directly and we will arrange an order for you as soon as possible!
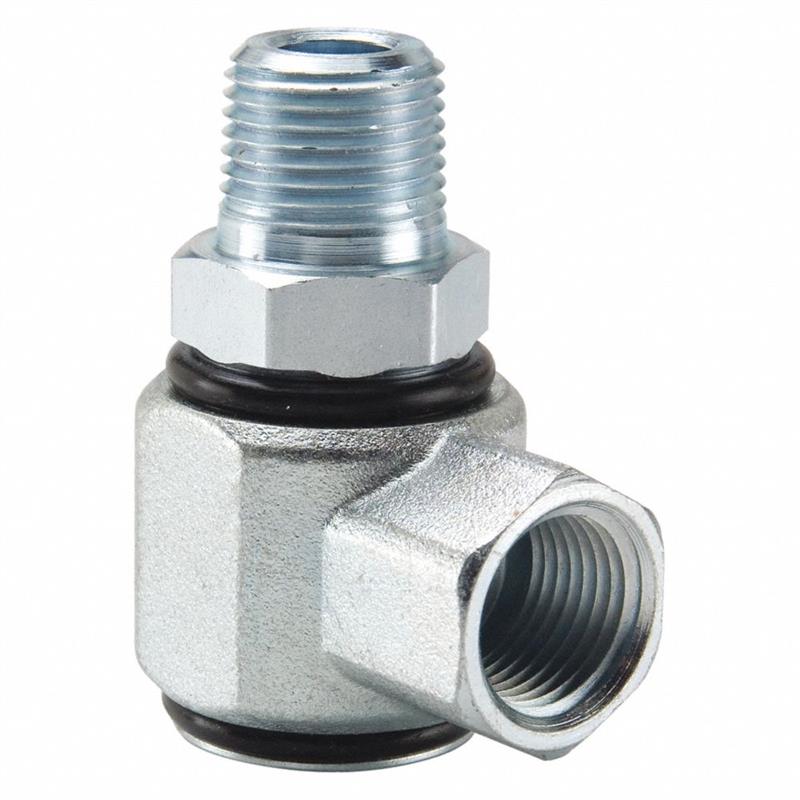
Male NPTF to Female NPSM
Hydraulic Live Swivel Fitting 90° Elbow, Male NPTF/Female NPSM, made of Carbon Steel.

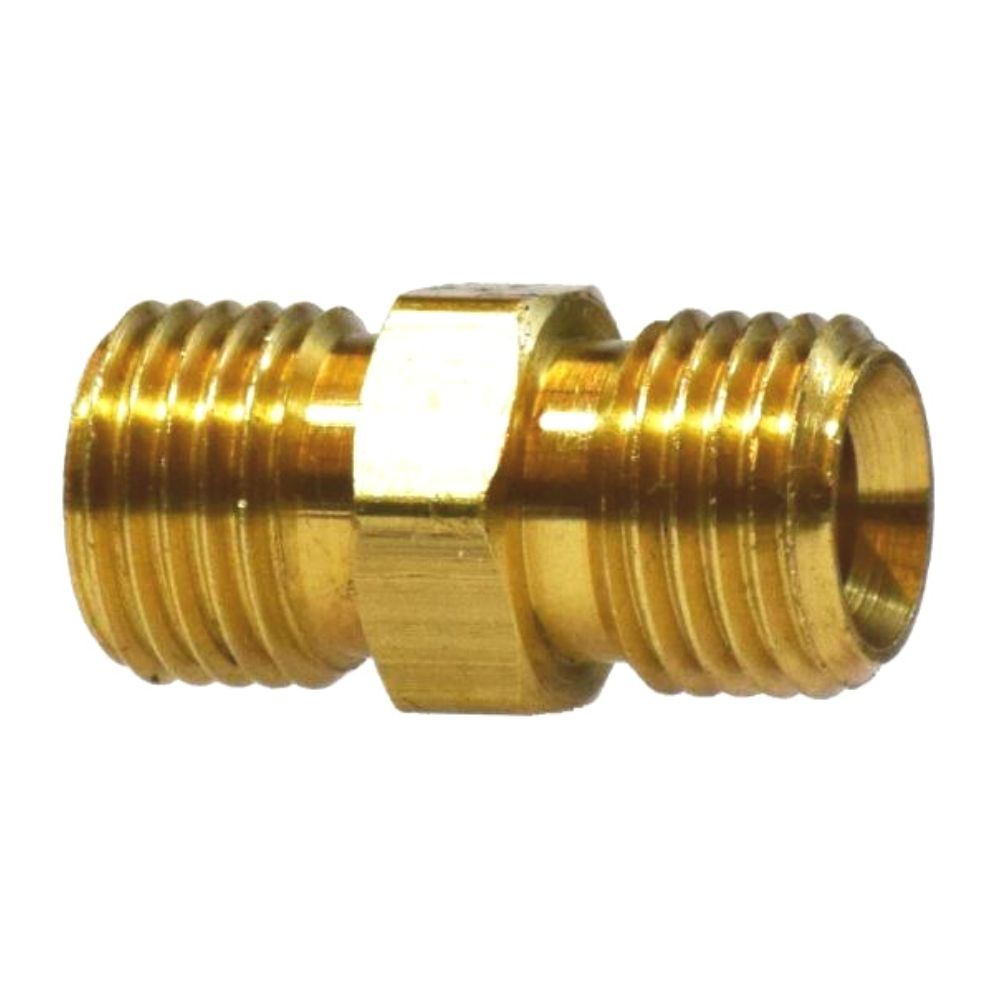
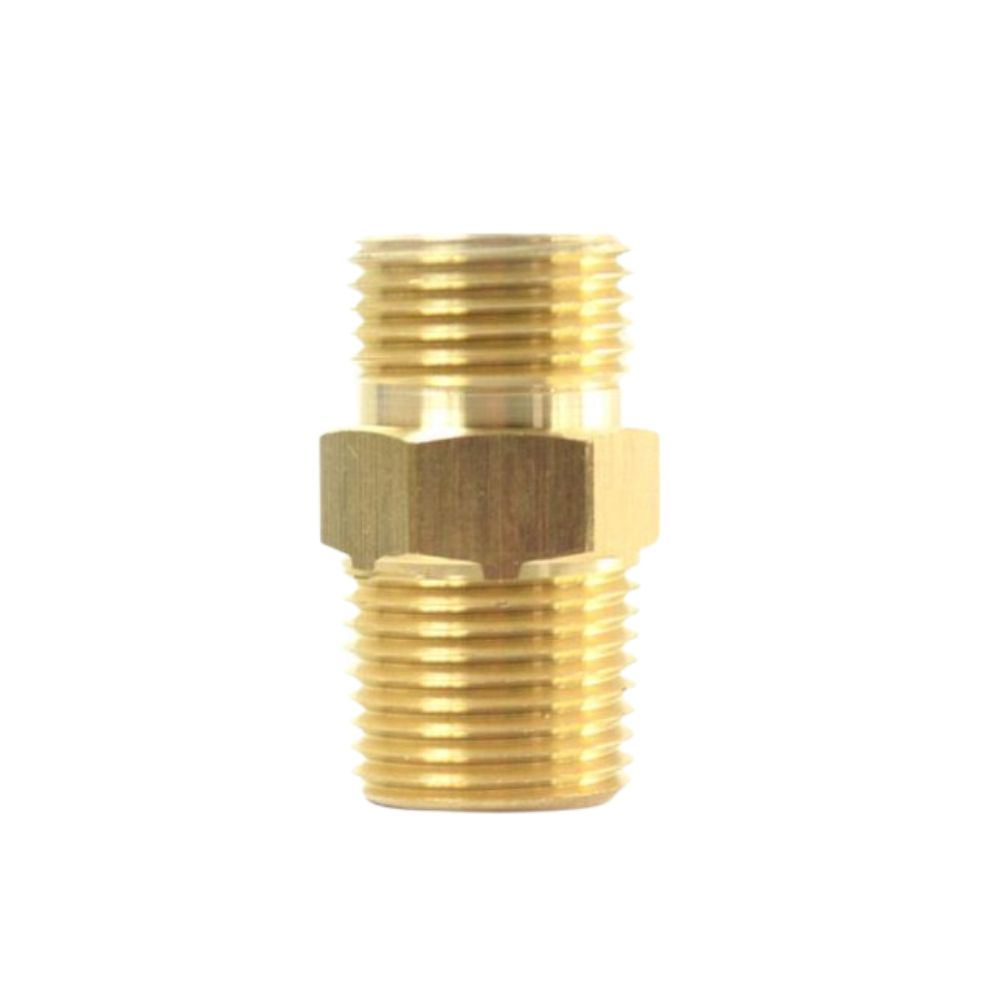
Male NPTF to Female NPTF
Hydraulic Swivel Fitting 90° Elbow, Male NPT, to Female NPT (including NPSM) .
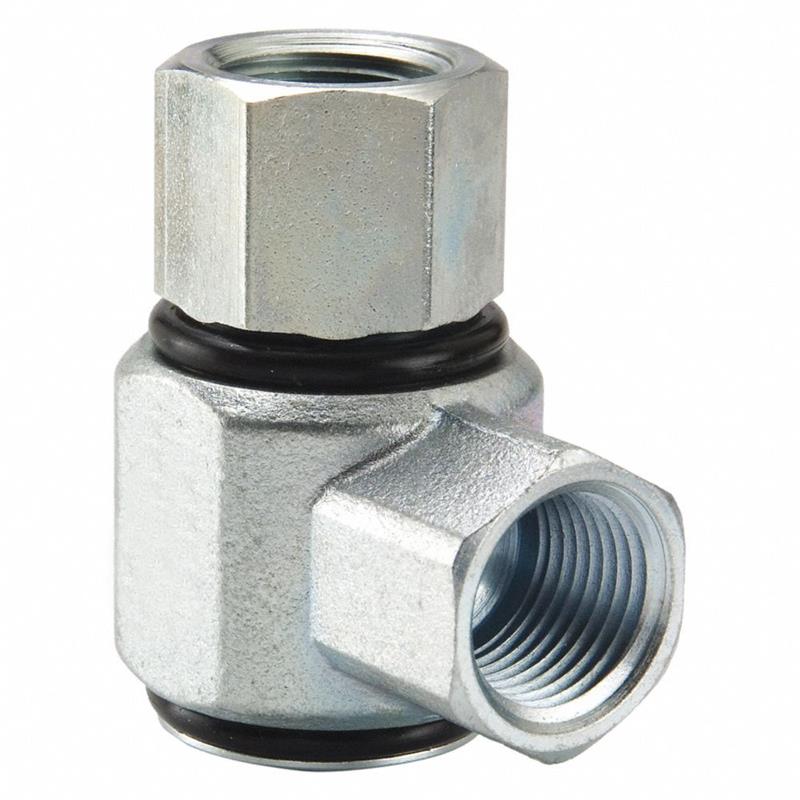

Female NPTF to Female NPTF
90° Elbow, Female NPTF to Female NPTF, made of carbon steel.
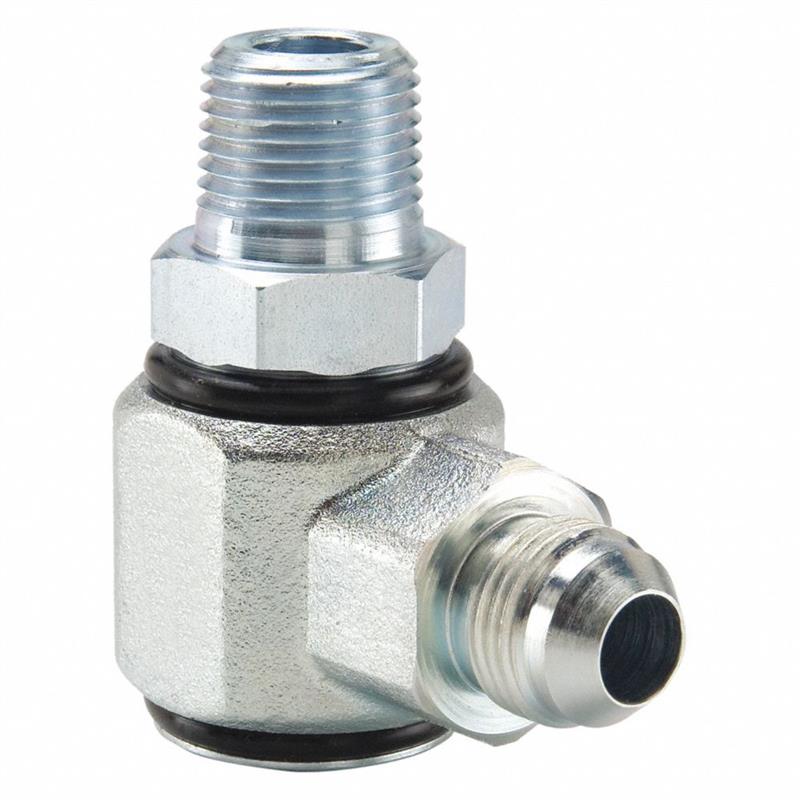

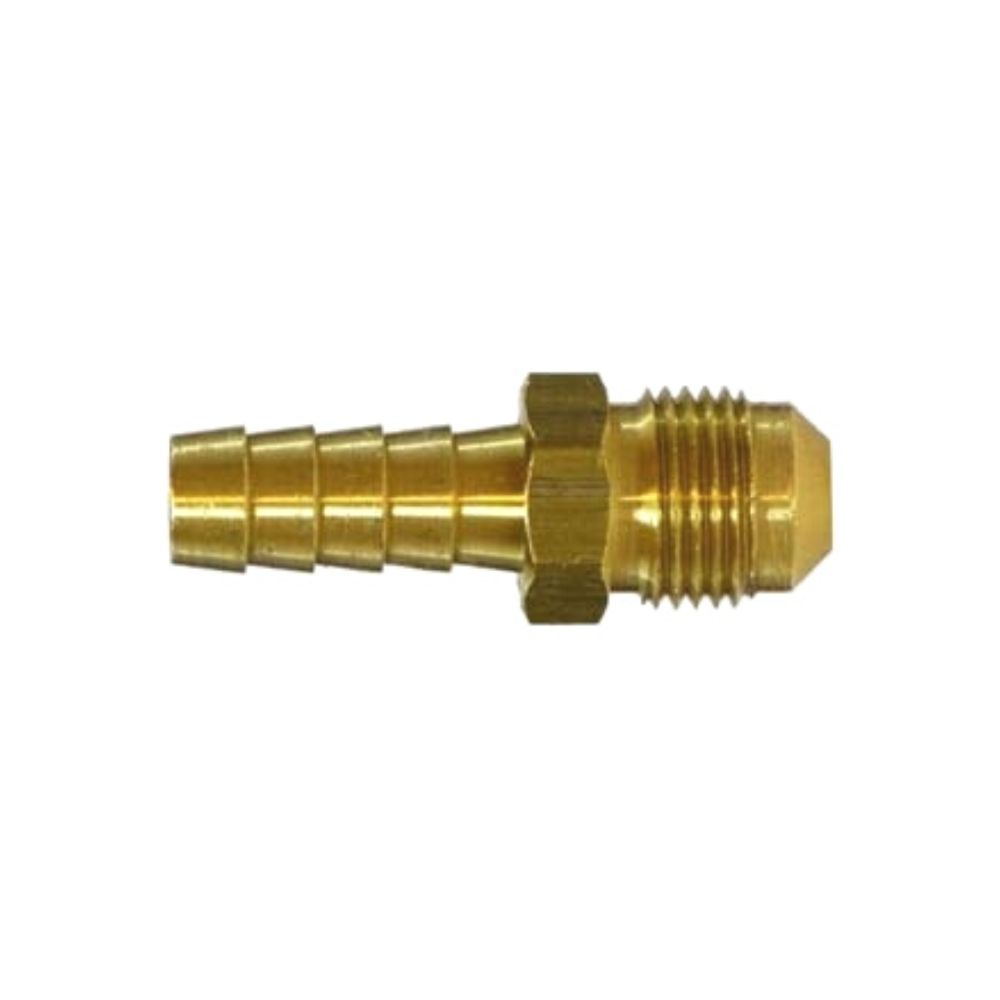
Male NPTF to Male JIC
DIN Metric Light hydraulic Fittings is available in mining, industrial, and construction.
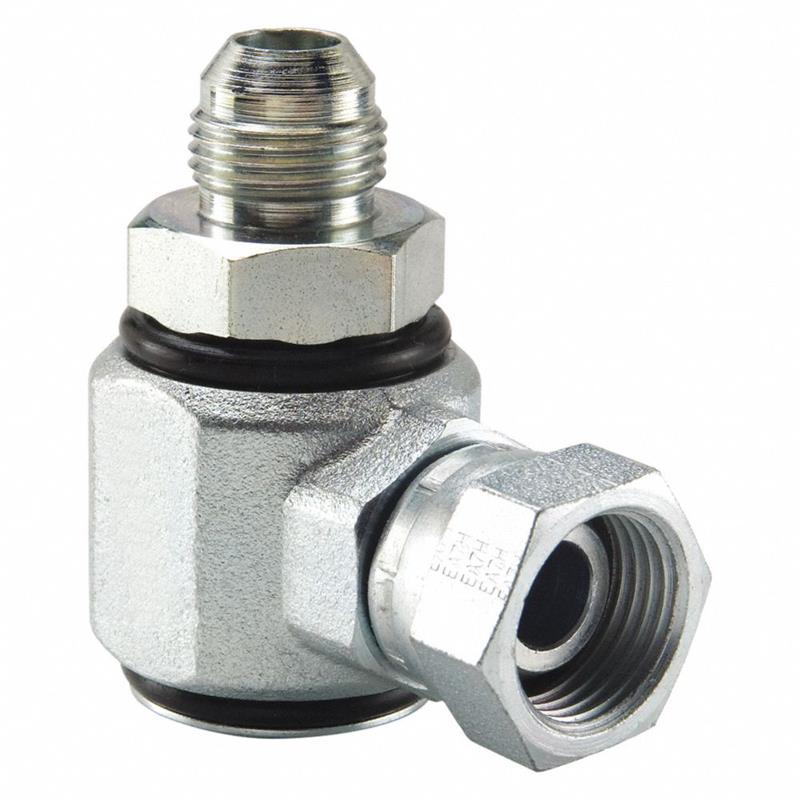

Male JIC to Female NPSM
Swivel fittings 90-degree elbow, Male JIC to Female NPSM Swivel
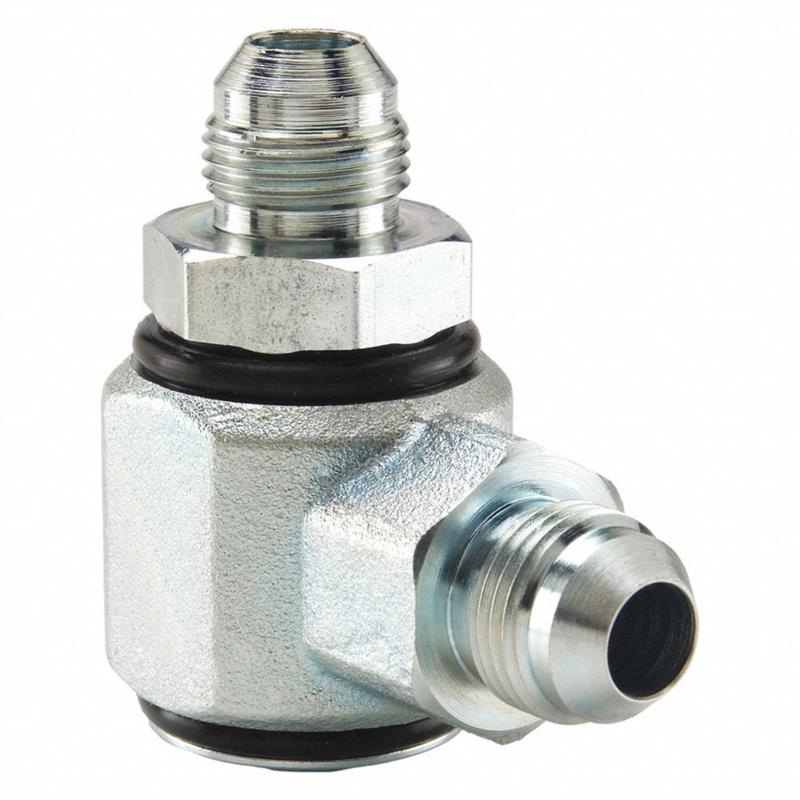

Male JIC to Male JIC
Hydraulic fittings elbow live swivels, Male JIC to Male JIC
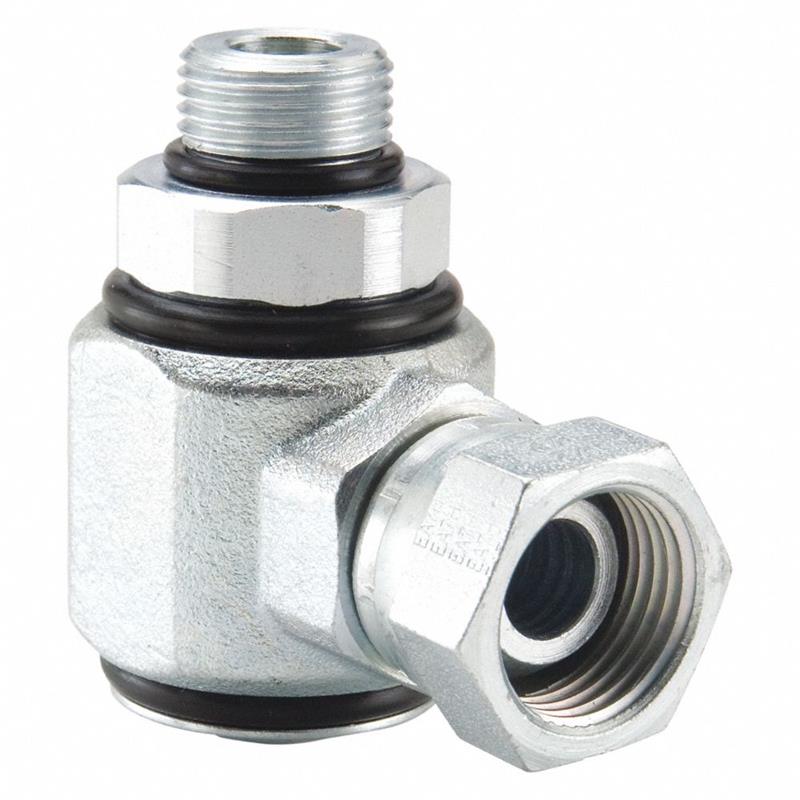

Male SAE to Female NPSM
Hydraulic live swivel fittings, Male SAE to Female NPSM Swivel
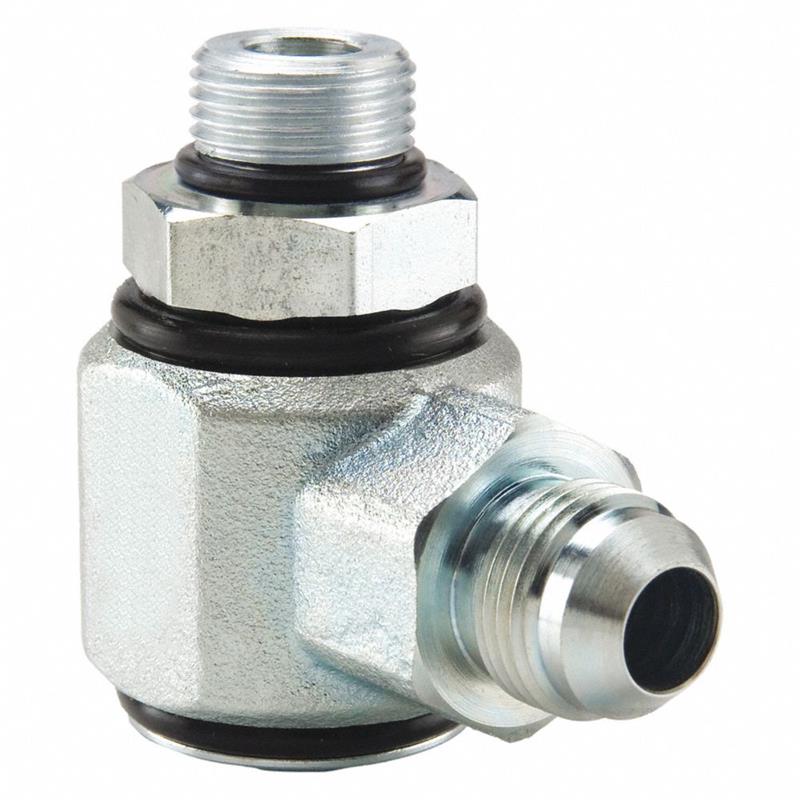

Male SAE to Male JIC
Live swivel fitting 90° Elbow, Male SAE to Female JIC
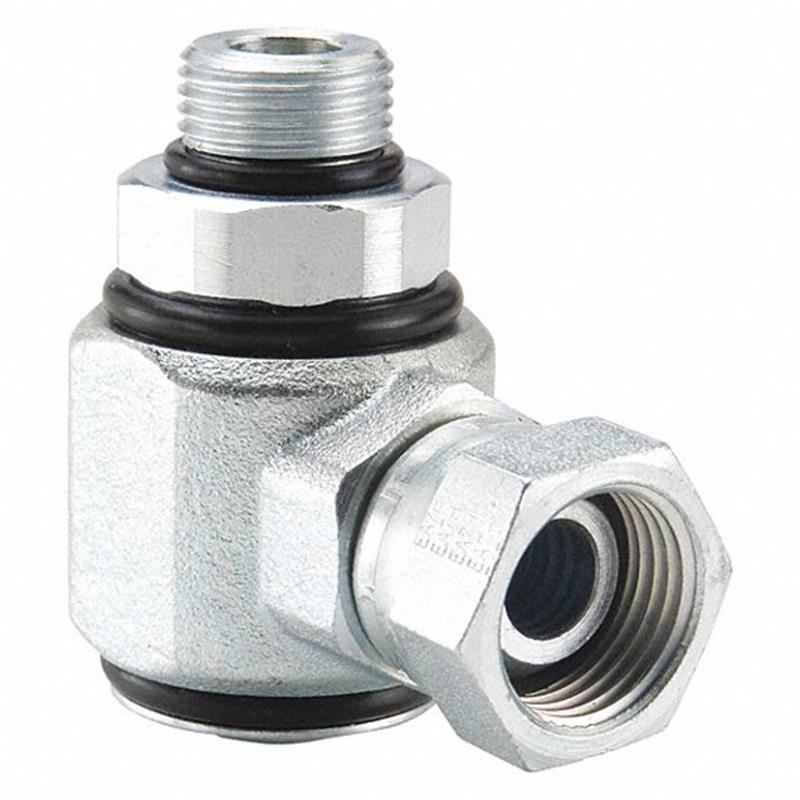

Male SAE to Female SAE
Hydraulic 90-degree elbow swivel fittings, Male SAE to Female SAE
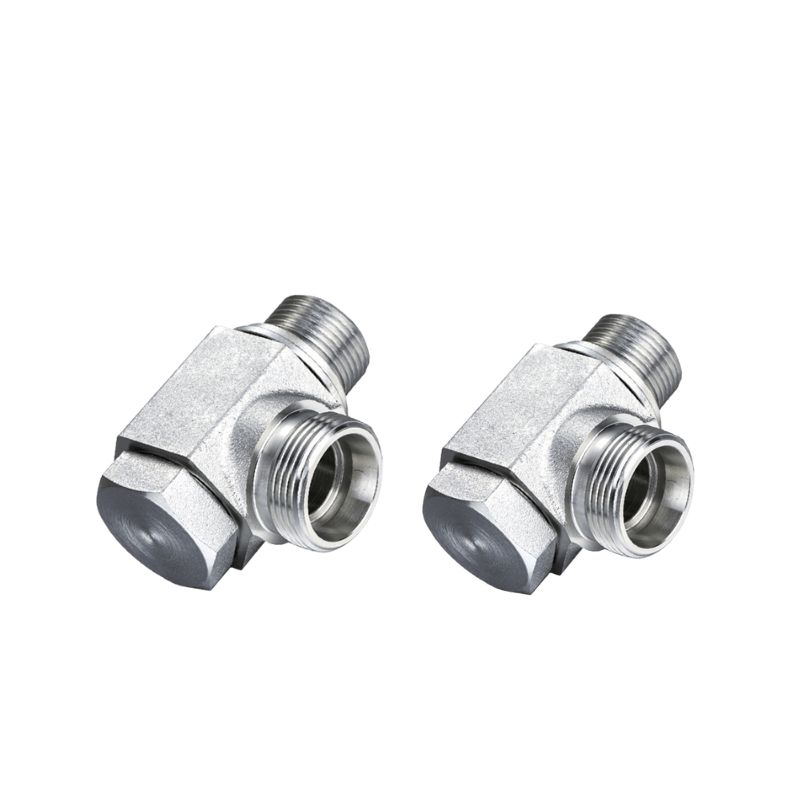

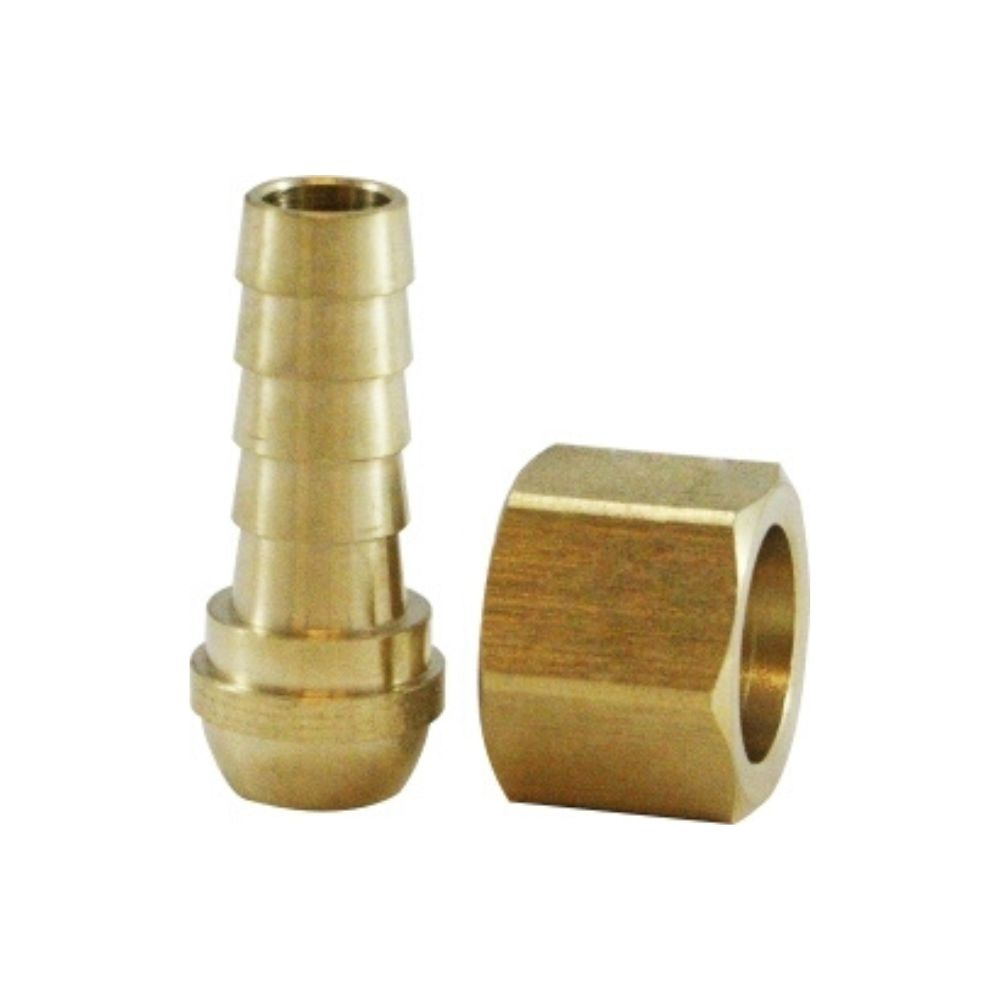
Metric thread ferrule swivel fittings
Metric threaded ferrules, transition fittings, for all kinds of hydraulic connections.
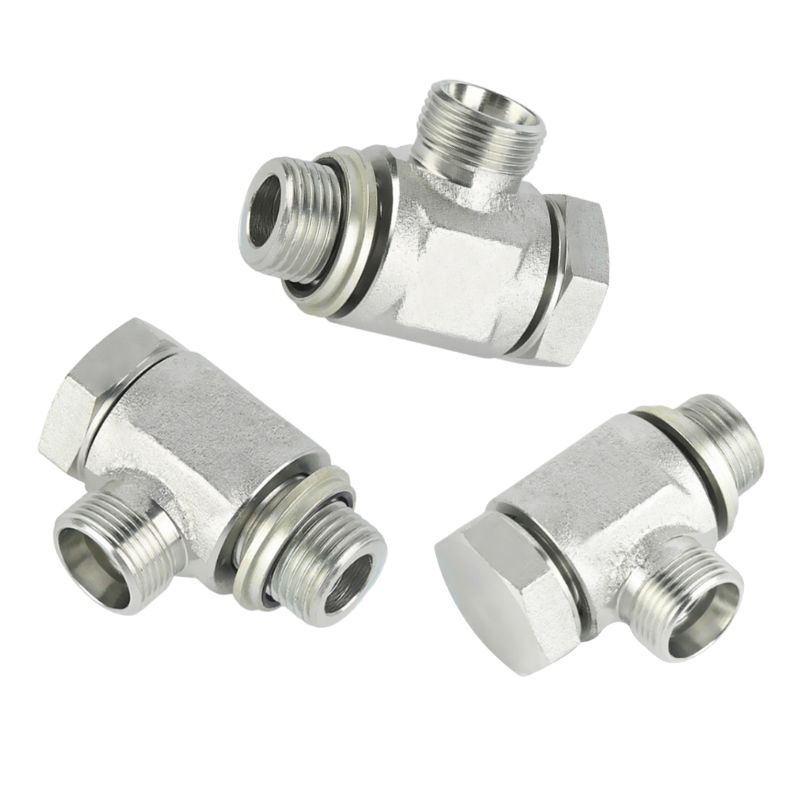

Metric banjo swivel hydraulic fitting
Metric banjo live swivel fitting, hydraulic transition fittings, for the machinery, transportation and industries.
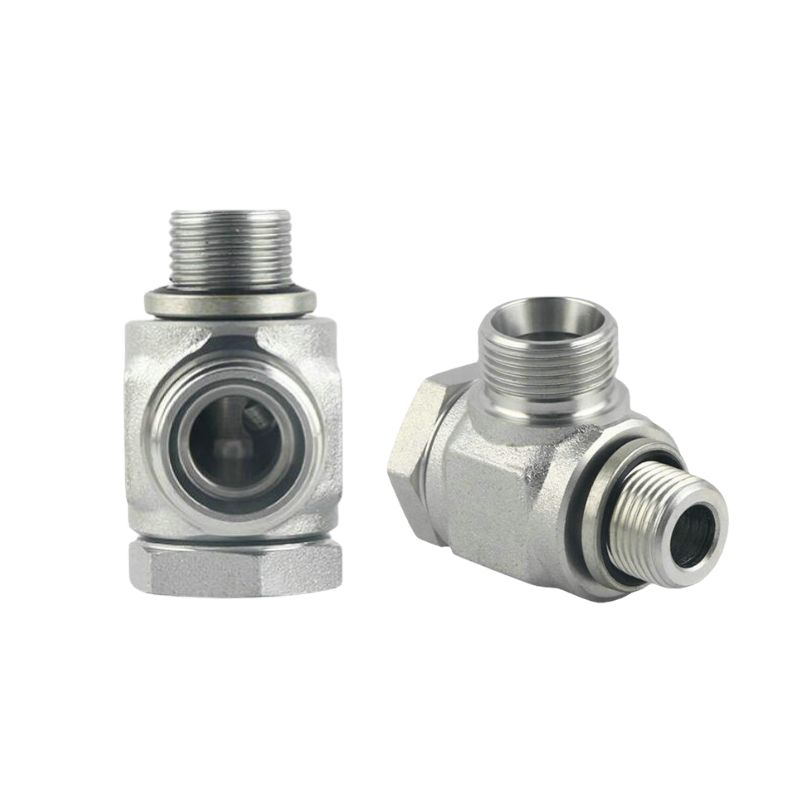

BSP banjo swivel hydraulic fitting
BSP elbow swivel fitting , with excellent structure and advanced design, are widely used in hydraulic and fluid transfer systems.

BSP thread ferrule swivel fittings
BSP hydraulic swivel fittings, hollow fittings , Suitable for hydraulic equipment, construction machinery.

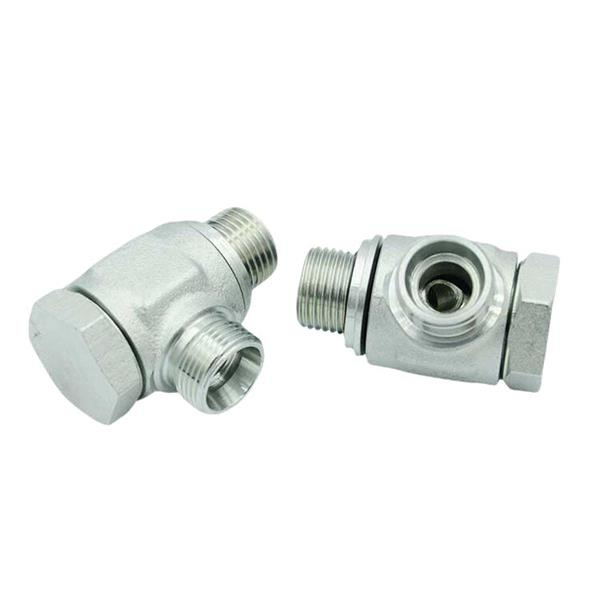
Right Angle High Pressure Swivel Fitting
Right Angle High Pressure Swivel Fitting, Elbow Swivel Fitting. Hydraulic Oil Pipe Right Angle Swivel Fitting.

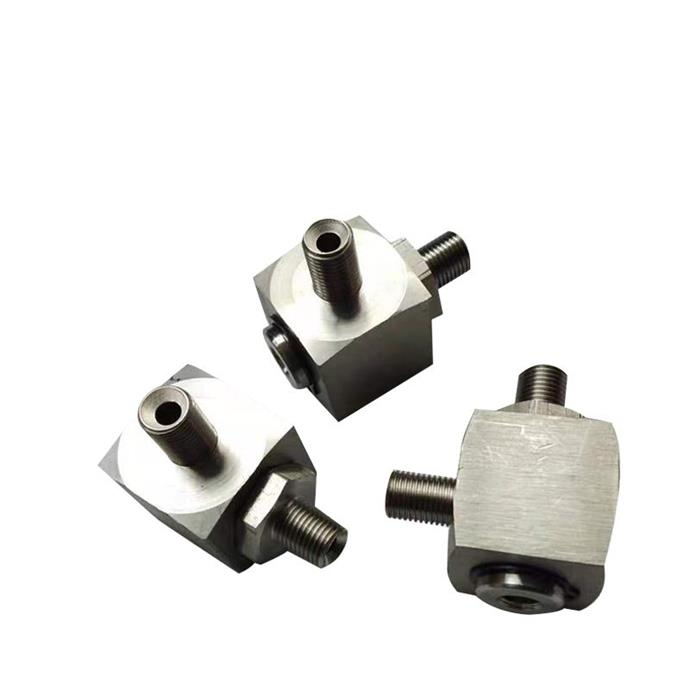
High pressure right angle swivel fitting
High-pressure hydraulic right-angle swivel fitting. Hydraulic Live swivel fitting.

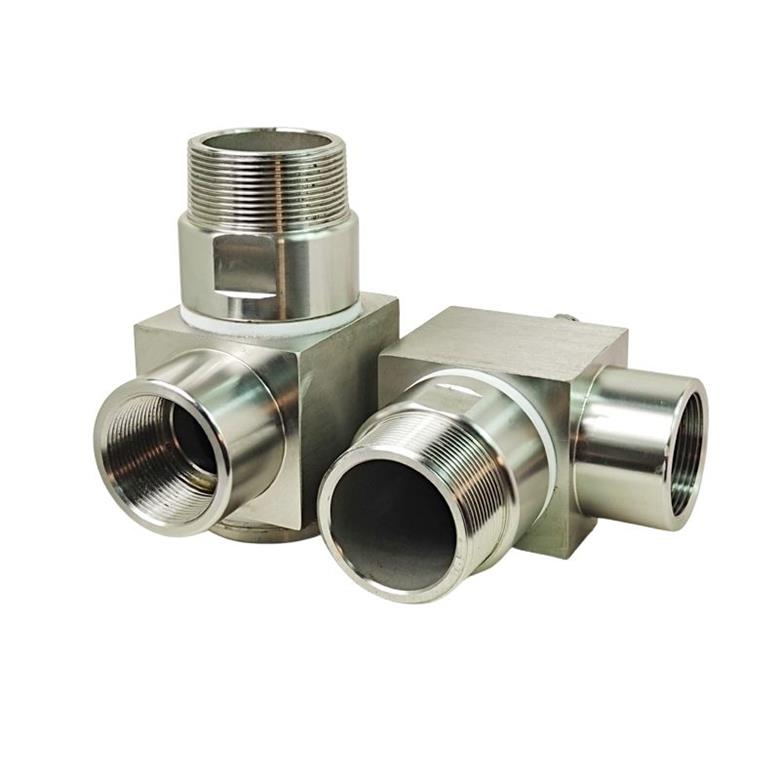
Hydraulic oil pipe swivel hydraulic fitting
Hydraulic swivel fitting universal fitting, 360 degree high pressure rotary fitting.
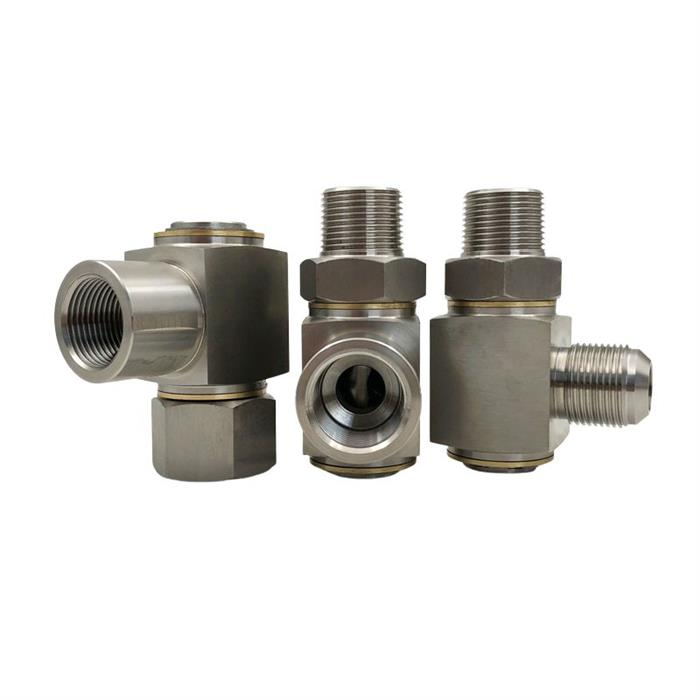

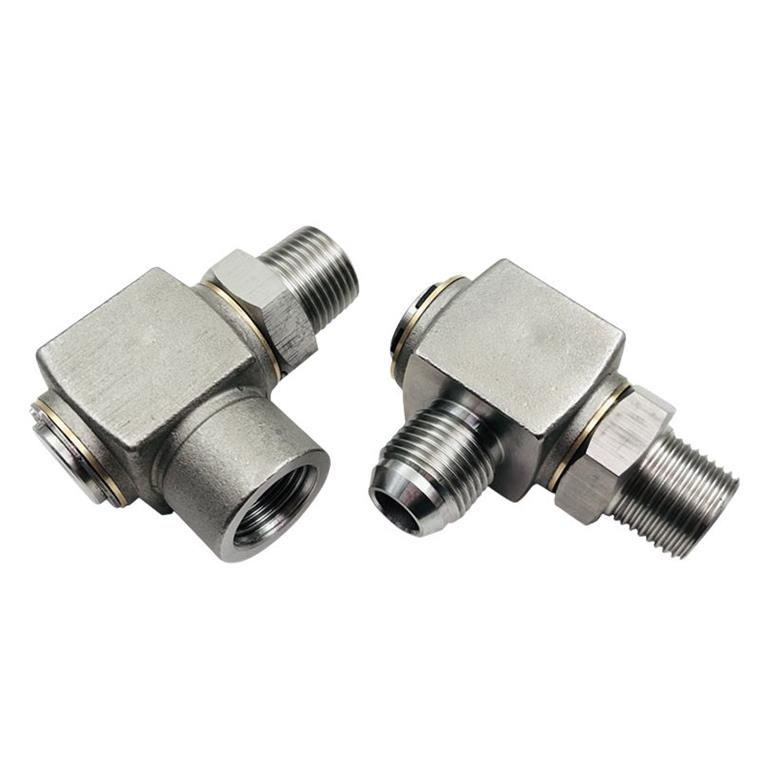
High speed right angle high pressure swivel fitting
High speed right angle, high pressure swivel fitting. Carbon steel swivel fitting. Hydraulic oil pipe right angle swivel fitting.
Hydraulic Live Swivel Fittings Features
Precision Engineering: Our hydraulic swivel joints are designed with precision threaded ends to ensure a safe and leak-free connection every time.
Material quality: Made from high-grade materials that resist corrosion and abrasion to extend the life of the fitting.
Compatibility: These threaded ends are compatible with a wide range of hoses and fittings, providing greater flexibility in your system design.
Up to 3,000 PSI: Designed to withstand high pressures, these fittings are rated up to 3,000 PSI, making them ideal for heavy-duty hydraulic applications.
Forged: Rotary joints are forged at high temperatures for added strength and rigidity to better withstand harsh environments.
Safety Measures: Includes built-in safety features to prevent pressure spikes and ensure consistent performance.


Durability: Superior material strength and high-pressure tolerance complement each other to ensure long-term reliability.
360 Degree Swivel: The swivel feature allows for a full 360-degree swivel, providing unmatched flexibility in system configuration.
Anti-tangle design: This feature prevents kinking and twisting of hoses, reducing maintenance time and costs.
Easy Installation: The swivel feature also simplifies the installation process, making it quick and easy.
10 RPM Capability: Designed for optimal performance, these couplings can operate at speeds up to 10 RPM without a significant increase in torque.
Smooth Operation: Even at the highest speeds, this design ensures smooth, consistent operation for increased system efficiency.
Adaptable: Suitable for both low and high-speed applications, it provides a versatile component for your hydraulic system.
Application
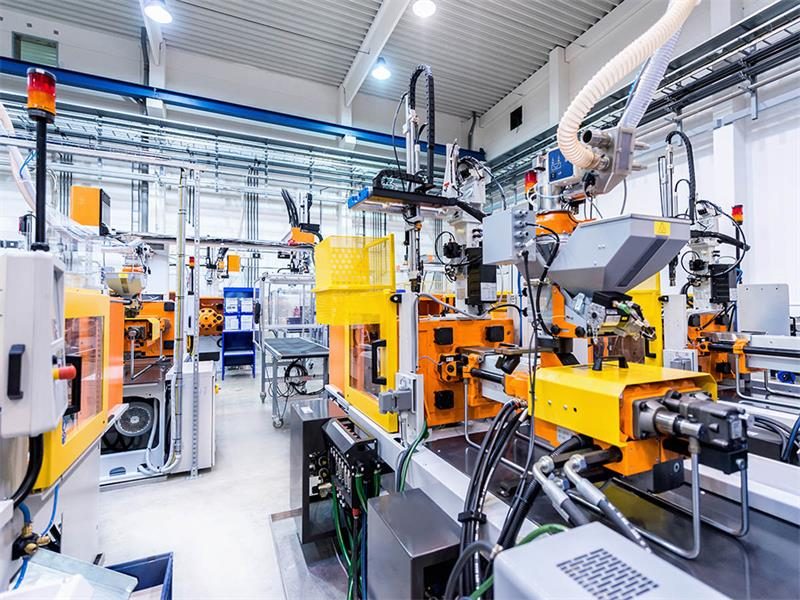

Industrial Machinery
With the ability to withstand high pressures, these live swivel fittings are indispensable in industrial environments where machinery operates under extreme conditions. The durability of our fittings ensures that your machinery has a longer operating life, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.

Construction Equipment
Ideal for construction machinery such as excavators, loaders, and cranes that work in harsh conditions. High-pressure tolerances and swivel functions help to increase the operating efficiency of the machine, so you can get the job done faster. Manufactured with safety in mind, our accessories ensure that your construction equipment operates safely, even in the harshest environments.

Automotive
Our hydraulic swivel fittings are designed for vehicles that require a high degree of reliability, such as trucks, buses, and specialty vehicles. These fittings ensure smooth and efficient operation of the hydraulic system, thus improving the overall performance of the vehicle. The swivel feature allows easier access to components, simplifying maintenance tasks and reducing labor costs.
Quality Control
Topa’s products undergo a variety of quality control procedures to ensure the quality of the live swivel hydraulic adapters.
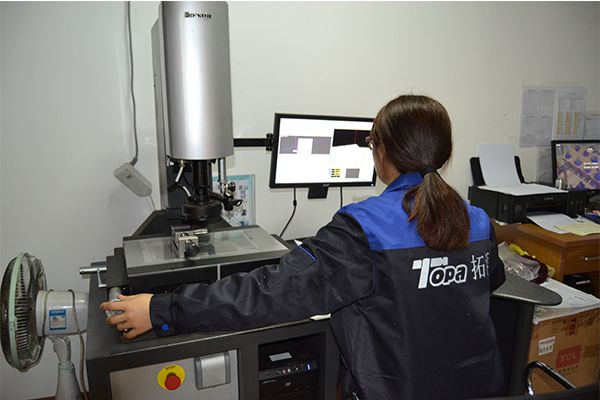

Size Inspection
Topa has a specialized image tester for checking hydraulic fitting thread dimensions.
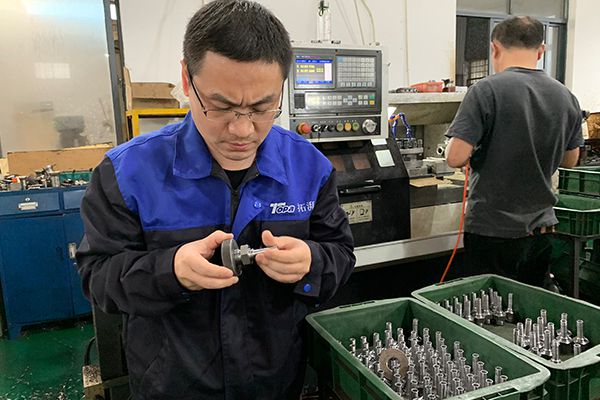

Thread Testing
Specialized operators will use hydraulic thread gauges to test fitting threads for compliance with use standards.
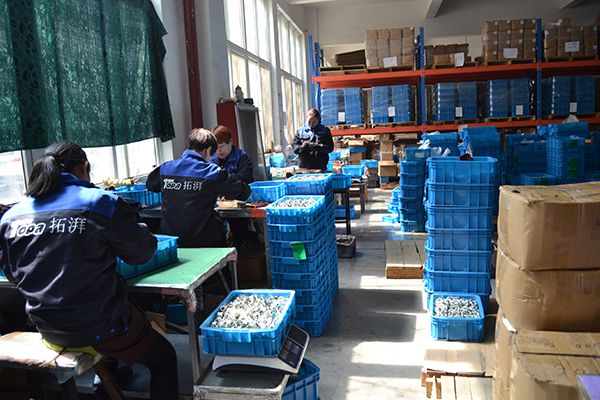

Fitting Assemble
Topa's employees install special caps on the threads of the fittings to protect the threads and then organize them neatly.
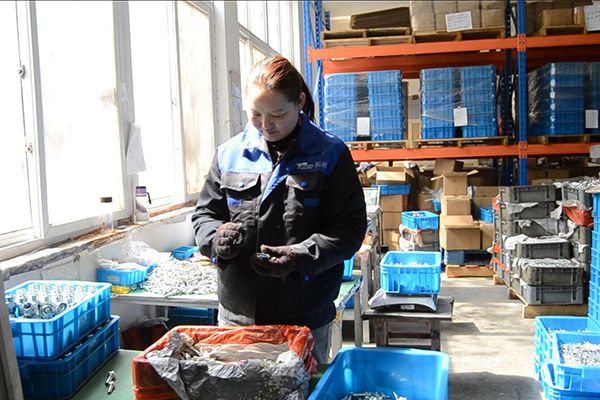

Check One by One
Specialized inspectors carefully check each fitting to ensure that the fitting is free of damage.
Our Factory
Topa-The Best Hydraulic Swivel Fittings Factory
China Hydraulic live swivel fittings manufacturer!
※ Unmatched Quality
Material Excellence: Made from high-grade materials, our Live Swivel Fittings are designed to resist wear, corrosion, and pressure spikes, ensuring long-term reliability.
Precision Engineering: With a focus on precision, these fittings offer secure, leak-free connections that you can rely on.
※ High-Performance Capabilities
High-Pressure Tolerance: Our fittings are engineered to withstand pressures up to 5,000 PSI, making them ideal for even the most demanding hydraulic applications.
360-Degree Swivel: The full 360-degree rotation allows for greater flexibility and movement, reducing the risk of hose kinks and twists.
※ Cost-Effectiveness
Affordable Quality: Manufactured in China, our Live Swivel Fittings offer a superior cost-performance ratio without compromising on quality.
Reduced Maintenance Costs: The durability and reliability of these fittings mean fewer replacements and less downtime, saving you money in the long run.

※ Versatility
Wide Range of Applications: From industrial machinery and automotive systems to construction equipment, these fittings are versatile enough to meet a variety of needs.
Compatibility: Designed to be compatible with a wide range of hoses and couplings, providing greater flexibility in your system design. And our swivels are compatible with all international brands such as Parker hydraulic live swivels, gates hydraulic live swivels, and eaton hydraulic swivel fitting.
※ Trusted Brand
Global Reach: With satisfied clients in the United States, Canada, Australia, and beyond, we have a proven track record of delivering quality products worldwide.
Expertise: With a team of 20 skilled professionals, we pride ourselves on our expertise and commitment to quality.
※ One-Stop Solution
Comprehensive Service: At Topa Hydraulic, we offer a one-stop service for all your hydraulic needs, from fittings to cylinders and beyond.
By choosing Topa Hydraulic Live Swivel Fittings, you’re not just making a purchase; you’re making an investment in quality, reliability, and efficiency.
Hot Sales
FAQ
What is the primary function of hydraulic swivel fittings?
The primary function is to prevent hose twisting and torque, allowing for greater flexibility and movement in hydraulic systems.
What materials are used in the construction of these fittings?
Our hydraulic swivel fittings are made from high-grade materials that are corrosion-resistant and designed for long-term durability.
What is the maximum pressure these fittings can withstand?
Our fittings are engineered to withstand pressures up to 3,000 PSI, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Do the fittings come with threaded ends?
Yes, our hydraulic swivel fittings come with precision-threaded ends to ensure a secure and leak-free connection.
What is the maximum speed at which these fittings can operate?
These fittings can operate at a maximum speed of 10 RPM without any significant increase in torque as the pressure escalates.
Where are hydraulic swivel fitting used?
Examples include grabs, forestry attachments, cranes and utility boom trucks, demolition shears and mobile excavators, etc.
How does the swivel functionality work?
The swivel feature allows for a full 360-degree rotation, offering unparalleled flexibility in system configuration and reducing the risk of hose kinks and twists.
How do these fittings contribute to operational efficiency?
The high-pressure tolerance and swivel functionality contribute to the machine’s operational efficiency, allowing for faster completion of tasks and reduced maintenance costs.
Are these fittings easy to install?
Yes, the design of these fittings allows for quick and easy installation, reducing labor costs and setup time.
Why should I choose Topa Hydraulic's swivel fittings?
Choosing our hydraulic swivel fittings means you’re investing in quality, durability, and efficiency. We offer a one-stop service for all your hydraulic needs and have a proven track record of delivering quality products worldwide.

























































